Does All Capsules Drops In Kazakhstan On Return After Every Mission?
Does all capsules drops in Kazakhstan on return after every mission?
Since the US Space Shuttle retired in 2011, we launch to and return from the Space Station with the Russian Space Agency. So yes, these capsules (the Soyuz) land in Kazakhstan (or surrounding regions). However, different spacecrafts have different reentry trajectories, depending on where they aim to land. As you might recall, the Apollo mission capsules landed in the ocean. Since Space-X and Boeing are currently building new vehicles so that we will also launch from the US again to get to the International Space Station, these spacecraft will return to the US. For example, you may have seen footage of Space-X cargo vehicles splashing down into the Pacific over the last few years. The Boeing Starliner plans to land on land instead of water. NASA is also currently building the Orion spacecraft, which will take us to destinations beyond low earth orbit (where the Space Station is), whether that be the Moon or Mars or another target. Orion will also splash down in the ocean.
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others

Soviet Cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev stuck in space during the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991
Unable to return home, he ended up having to stay in space until further notice.
The cosmonaut eventually returned back to earth on March 25, 1992, after 10 months in orbit - to a nation that was very different to what it was when he had left. The Soviet Union had fractured into 15 nations, presidents had changed, and even his hometown of Leningrad had become St. Petersburg.
Interestingly, at the time, Krikalev was supposed to serve in the military reserves, and was almost issued a warrant for desertion – before the army realised that their reserve soldier was not even on the planet.
Does space have a standard time or do you rely on the time zones on Earth while you are in space?
Great question. Really it is up to the particular space agency/mission which time zone they use. For example, since the International Space Station is a collaboration between NASA, the Russian Space Agency, the European Space Agency, the Japanese Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency, we came up with the compromise of operating on Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). So, Space Station time is the same as London time! The International Space Station orbits our planet every 90 minutes, so of course we’re transiting across multiple time zones constantly.
Here’s a great example of the kinds of experiments astronauts perform on the International Space Station, just like I talked about in Episode 19! I absolutely want to high-five whoever called is ISS-CREAM.
From Frozen Antarctica to the Cold Vacuum of Space
A new experiment that will collect tiny charged particles known as galactic cosmic rays will soon be added to the International Space Station. The Cosmic Ray Energetics And Mass for the International Space Station payload, nicknamed ISS-CREAM, will soon be installed in its new home on the Station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility. ISS-CREAM will help scientists understand more about galactic cosmic rays and the processes that produce them.

Wait, what are cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are pieces of atoms that move through space at nearly the speed of light. Galactic cosmic rays come from beyond our solar system.

They provide us with direct samples of matter from distant places in our galaxy.
Why do these things go so fast?
Galactic cosmic rays have been sped up by extreme processes. When massive stars die, they explode as supernovas. The explosion’s blast wave expands into space along with a cloud of debris.

Particles caught up in this blast wave can bounce around in it and slowly pick up speed. Eventually they move so fast they can escape the blast wave and race away as a cosmic ray.
Where can we catch cosmic rays?
Cosmic rays are constantly zipping through space at these super-fast speeds, running into whatever is in their path – including Earth.

But Earth’s atmosphere is a great shield, protecting us from 99.9 percent of the radiation coming from space, including most cosmic rays. This is good news for life on Earth, but bad news for scientists studying cosmic rays.
So… how do you deal with that?
Because Earth has such an effective shield against cosmic rays, the best place for scientists to study them is above our atmosphere – in space. Since the 1920s, scientists have tried to get their instruments as close to space as possible. One of the simplest ways to do this is to send these instruments up on balloons the size of football stadiums. These balloons are so large because they have to be able to both lift their own weight and that of their cargo, which can be heavier than a car. Scientific balloons fly to 120,000 feet or more above the ground – that’s at least three times higher than you might fly in a commercial airplane!

Credit: Isaac Mognet (Pennsylvania State University)
Earlier versions of ISS-CREAM’s instruments were launched on these giant balloons from McMurdo Station in Antarctica seven times, starting in 2004, for a total of 191 days near the top of the atmosphere. Each of these flights helped the team test their hardware and work towards sending a cutting-edge cosmic ray detector into space!
How is going to space different than flying balloons?
Balloon flights allowed the team to collect a lot of cosmic rays, but even at 120,000 feet, a lot of the particles are still blocked. Scientists at the University of Maryland, College Park, who operate ISS-CREAM, expect to get about 10 times as much data from their new home on the International Space Station.

That’s because it will be both above the atmosphere and fly far longer than is possible with a balloon. As you might imagine, there are large differences between flying something on a balloon and launching it into space. The science instruments and other systems had to be changed so ISS-CREAM could safely launch on a rocket and work in space.
What will ISS-CREAM do?
While on the space station, ISS-CREAM will collect millions of cosmic rays – electrons, protons and atomic nuclei representing the elements found in the solar system. These results will help us understand why cosmic rays reach the wicked-fast speeds they do and, most important, what limits those speeds.
ISS-CREAM launches to the International Space Station aboard the latest SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, targeted to launch August 14. Want to learn more about ISS-CREAM and some of our scientific balloons? Check out our recent feature, NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program Reaches New Heights.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Stars are too distant to really peer at and they have all that radiation and heat and blinding light and such so it’s doubtful that we will ever be able to prod the Sun, but astronomers can certainly classify what stars we’ve been able to observe! This is the first part of a two-part series on star classification systems. This podcast focuses on variable stars, how they were discovered, the awesome women who started developing the basis of a major star classification system, and what variable stars did for our understanding of the universe.
There is a lot of technical talk and I did my best to make it comprehensible but you can absolutely hit me up with questions if you have them! I’m also on Twitter at @HDandtheVoid if you’d rather ask me there. And go ahead and check out the podcast on iTunes, rate it or review it if you’d like, and subscribe! I’ll always post all the extras here on tumblr but iTunes might be more convenient for downloading and podcast apps and all that good stuff.
Below the cut is some elaboration on the episode itself, including my sources, music credits, a BIG glossary, a quote on women and emotional labor that really hits home for me, and a transcript. I mention a couple of books and quote a couple people in this episode so if you want to see that written down, those sources are there as well. Let me know what you think of this episode, let me know what you think I should research next*, tell me a fun space fact… anything’s helpful!
*(The June 19th podcast is already set, it’s going to be part 2 on star classifications, but in July I could start talking about things like spectroscopy, planets, dark matter, or I have a book in at the library on longitude.)
Glossary:
arcsecond - an infinitesimal measurement of a degree; in 1 degree there are 3,600 arcseconds.
cosmic distance measurements: light-years - a way to imagine distance scales on an astronomical level; the distance light can travel in one year, or about 6 trillion miles. parsecs - a measurement of distance on an astronomical scale; the distance to a star that shifts by one arcsecond from one side of Earth’s orbit to the other. It’s more common than using light-years when discussing deep space astronomy. One parsec is about 19 trillion miles (30 trillion kilometers), a bit over 3 light-years.
magnitude - the measurement of a star’s brightness as seen from earth. The brighter it is, the lower its magnitude value; the Sun has an apparent magnitude of -27.
Malmquist Bias - the stars that are visible in a cluster are the brightest ones. Astronomers rely on them to compute average luminosity, but the fact that they’re the brightest ones inevitably skews the results.
parallax - the apparent shift of an object when viewed through two different lines of sight.
radial velocity - the speed at which a star is moving away from or towards Earth.
standard candle - a kind of celestial object that has a known luminosity due to some characteristic that the entire class of objects possesses.
stellar photometry - measuring and recording the magnitude of stars.
triangulation - a technique to measure the distance of an object by observing it from two different locations, knowing the distance between both observation locations and measuring the angle at which the distant object moves (its parallax angle).
variable stars: variable stars - stars that change brightness. Reasons for the brightness changes vary, and certain types of variable stars can be used to determine relative distance. They are either intrinsic (when a change in brightness is caused by a star’s own physical changes, like pulsation or eruption) or extrinsic (when the variance has an external cause, such as an eclipse of one star by another or stellar rotation). Cepheid variables - variable stars with a period between 1 and 70 days, with light variations from 0.1 to 2 magnitudes. They’re massive, with a high luminosity and are usually classified between F and G or K. They obey the period-luminosity relationship and played a major part in calculating distances to far-away galaxies as well as helping to determine the age of the Universe. eclipsing binaries - binary systems of stars where the components regularly eclipse one another, causing an apparent decrease in the brightness of the system. irregular variables - variable stars, typically red giants, without a measurable period to their luminosity. Long Period Variables - LPVs have periods ranging from 30 to 1,000 days. They’re red giants or supergiants, typically classified M, R, C, or N. There are subclasses, too: Mira, which have light variations of more than 2.5 magnitudes and are the future evolution of our own star, the Sun; and semiregular, which have some regular periods and some irregular light variation and have light variations less than 2.5 magnitudes. RR Lyrae - variable stars with a period of 0.05 to 1.2 days and a light variation between 0.3 and 2 magnitudes. They’re older and smaller than Cepheids, and are white giant stars typically classified as A. RV Tauri - variable stars that have periods between 30 and 150 days, light variation up to 3 magnitudes, and possible cycle variations that can be hundreds or thousands of days long. They’re yellow supergiants classified between G and K.
cataclysmic variables: dwarf nova - a close binary system of a red dwarf, a white dwarf, and an accretion disk around the white dwarf. They brighten by 2 to 6 magnitudes depending on the stability of the disk, which loses material to the white dwarf. nova - a close binary system of a white dwarf and a secondary star that’s a little cooler than the Sun. The system brightens 7 to 16 magnitudes in 1 to 100 days, and then the star fades slowly to the initial brightness over a period of several years or decades. At maximum brightness, it’s similar to an A or F giant star. Recurrent novae are similar to this category of variable but have several outbursts during their recorded history. R Coronae Borealis - an eruptive variable, a supergiant star that is hydrogen-poor and carbon-rich and spends most of its time at maximum light, fading as much as 9 magnitudes at irregular intervals. Most often classified between F and K or R. supernova - a massive star that explodes with a magnitude increase of 20 or more. Supernovae have led us to realize that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating. symbiotic stars - close binary systems of a red giant and a hot blue star. They have nova-like outbursts up to 3 magnitudes.
Script/Transcript
Sources:
What stars are made of via NASA
Stars, Cepheid Variable by T. Lloyd Evans via the California Institute of Technology aka CalTech
Variable stars via the Australia Telescope National Facility
American Association of Variable Star Observers website. I used a couple of pages from this one but the whole organization is kinda on the nose.
Stellar magnitude via EarthSky
A star magnitude scale via Harvard
Harvard Observatory’s Astronomical Photographic Plate Collection, which has a history of the collection and the women computers.
Definitions and differences for parsecs and light-years, and a description of parallax and triangulation via EarthSky
Standard candle breakdowns via some magical wonderful person with the best accessible online science book project I have ever encountered. Mad props to whoever is doing this, it’s a noble cause.
Info on Walter Baade via the Online Archives of California
A very math-y breakdown of the Malmquist Bias in the article “Observational Selection Bias Affecting the Determination of the Extragalactic Distance Scale” by P. Teerikorpi, published 1997
Johnson, George. Miss Leavitt’s Stars. Atlas Books: NY, 2005.
Henrietta Swan Leavitt quote: “It is worthy of notice [that] the brighter variables have the longer periods” (38).
“If a theory or observation seemed to suggest that we, the observers, happen to occupy an exalted place in the heavens, then it was probably wrong” (110)
Edwin Hubble quote: “With increasing distance, our knowledge fades, and fades rapidly. Eventually, we reach the dim boundary—the utmost limits of our telescopes. There, we measure shadows, and search among ghostly errors of measurements for landmarks that are scarcely more substantial” (130)
Pickover, Clifford A. “Leavitt’s Luminosity Law.” Archimedes to Hawking: Laws of Science and the Great Minds Behind Them. Oxford UP: NY, 2008. 475.
Soba, Dava. The Glass Universe: How the Ladies of the Harvard Observatory Took the Measure of the Stars. Viking: New York, 2016.
From Claire Messud’s The Woman Upstairs (I haven’t read the book, I just collect quotes, so this isn’t me endorsing the book; I know nothing about it except this paragraph): “I’m a good girl, I’m a nice girl, I’m a straight-A, strait-laced, good daughter, good career girl, and I never stole anybody’s boyfriend and I never ran out on a girlfriend, and I put up with my parents’ shit and my brother’s shit, and I’m not a girl anyhow, I’m over forty fucking years old, and I’m good at my job and I’m great with kids and I held my mother’s hand when she died, after four years of holding her hand while she was dying and I speak to my father every day on the telephone–every day, mind you, and what kind of weather do you have on your side of the river, because here it’s pretty gray and a bit muggy too? It was supposed to say ‘Great Artist’ on my tombstone, but if I died right now it would say ‘such a good teacher/daughter/friend’ instead; and what I really want to shout, and want in big letters on that grave, too, is FUCK YOU ALL.”
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: 'River Man’ by Nick Drake off his album Five Leaves Left.
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
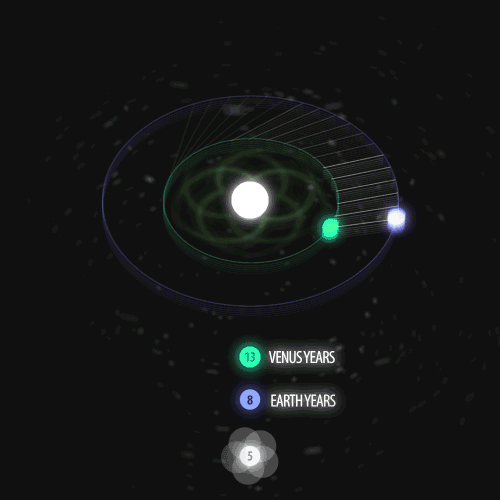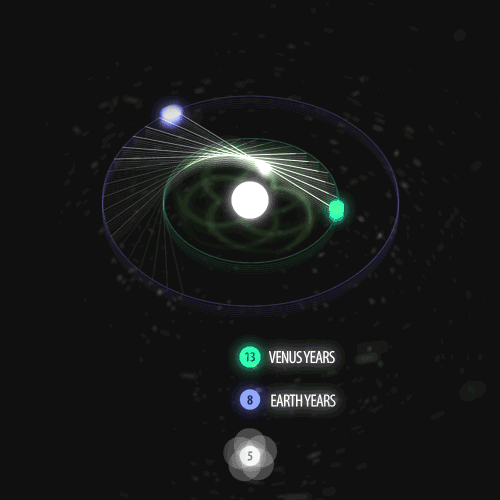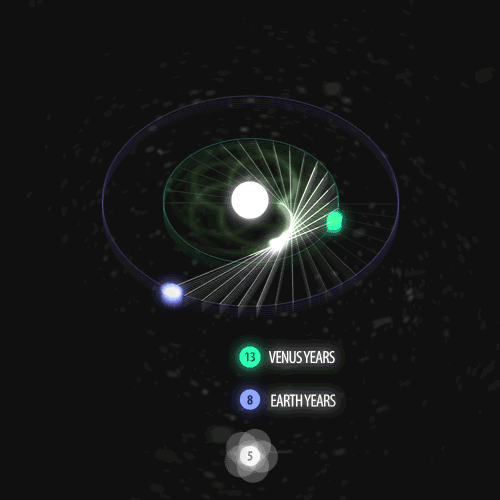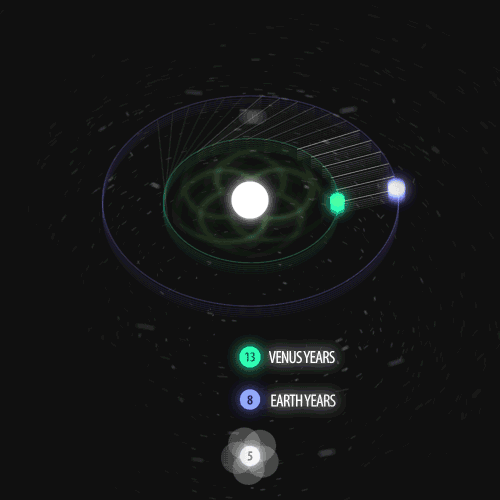
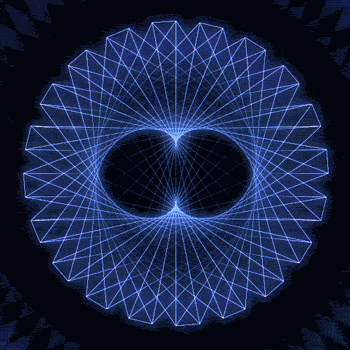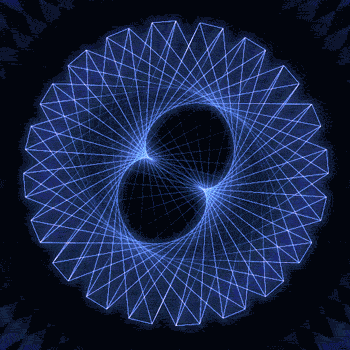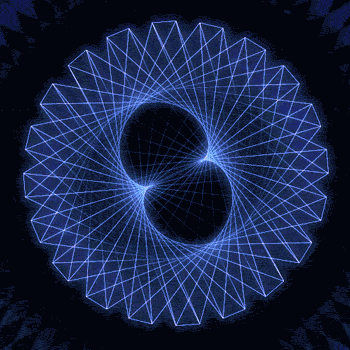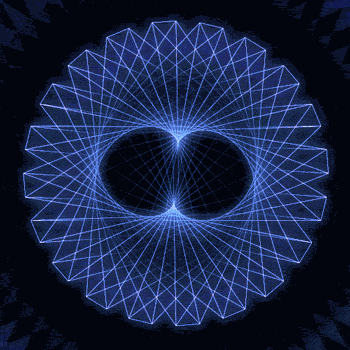
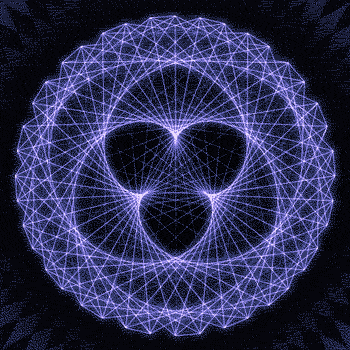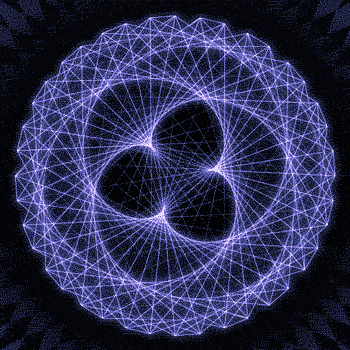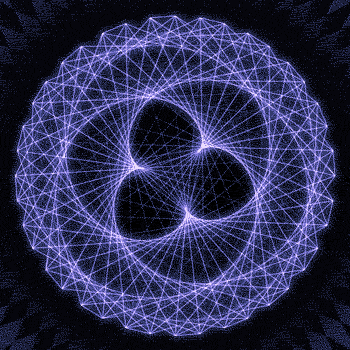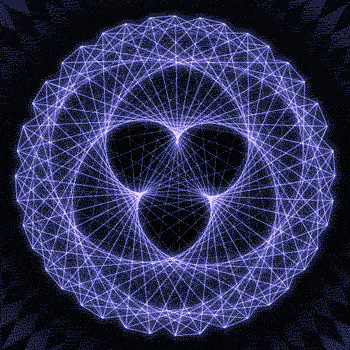


Fibonacci you crazy bastard….
As seen in the solar system (by no ridiculous coincidence), Earth orbits the Sun 8 times in the same period that Venus orbits the Sun 13 times! Drawing a line between Earth & Venus every week results in a spectacular FIVE side symmetry!!
Lets bring up those Fibonacci numbers again: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34..
So if we imagine planets with Fibonacci orbits, do they create Fibonacci symmetries?!
You bet!! Depicted here is a:
2 sided symmetry (5 orbits x 3 orbits)
3 sided symmetry (8 orbits x 5 orbits)
5 sided symmetry (13 orbits x 8 orbits) - like Earth & Venus
8 sided symmetry (21 orbits x 13 orbits)
I wonder if relationships like this exist somewhere in the universe….
Read the Book | Follow | Hi-Res -2- -3- -5- -8-
This has been going on since 1995! There are so many pictures! I gotta check these out but it will take hours. Maybe treat myself to like ten a day? It’s a better way to wake up than checking Facebook right now, I like this plan.










Cassini prepares for final orbital “Grand Finale” at Saturn.
Erik Wernquist, the same filmmaker who created 2014’s “Wanderers” and a stunning New Horizons promotional film in 2015, has created a new video highlighting NASA’s Cassini mission’s final days at Saturn. The Cassini spacecraft will begin its final series of orbits to cap a 13-year groundbreaking science mission known as the Grand Finale. For the first time ever in Cassini’s time at Saturn, the spacecraft will fly in between the planet’s rings and atmosphere. No spacecraft has ever before flown in this region of any of the solar system’s ringed planets. After 20 orbits, Cassini will dive into Saturn’s upper atmosphere September 15 where it will be destroyed. In 2008, mission managers explored a range of End of Mission scenarios that would protect Saturn’s moon’s from Earthly contaminants before ultimately deciding on atmospheric reentry. Cassini began her End of Mission manoeuvres on November 26, 2016, when it began the first of 20 ring-grazing orbits. A close flyby of Titan April 22 will alter the spacecraft’s trajectory to begin the first of 23 orbits in the Grand Finale, which will begin April 26.

Cassini launched from Earth on October 20, 1997, and entered Saturn orbit July 1, 2004. 16 days later, the European-built Huygens probe attached to the spacecraft landed on Titan, becoming the first probe to land in the outer solar system. Originally scheduled for a four-year mission ending in 2008, Cassini received two mission extensions in 2008 and 2010, with the latter ending in 2017. With the spacecraft’s fuel reserves low, the Cassini team decided to end the mission. P/C: JPL/Erik Wernquist

The 10-billion-year life cycle of the Sun, illustrated by David Meltzer for National Geographic, May 1974.
-
 john-erby liked this · 3 years ago
john-erby liked this · 3 years ago -
 2reputationpegacorns liked this · 4 years ago
2reputationpegacorns liked this · 4 years ago -
 theartisticscientistsworld liked this · 5 years ago
theartisticscientistsworld liked this · 5 years ago -
 cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago
cosmofrog liked this · 5 years ago -
 fcirfolk liked this · 7 years ago
fcirfolk liked this · 7 years ago -
 mariner52156 liked this · 7 years ago
mariner52156 liked this · 7 years ago -
 nineteenen liked this · 7 years ago
nineteenen liked this · 7 years ago -
 chabeinator liked this · 8 years ago
chabeinator liked this · 8 years ago -
 galowglass reblogged this · 8 years ago
galowglass reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 0800heart liked this · 8 years ago
0800heart liked this · 8 years ago -
 fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago
fillthevoid-with-space reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dizzyfingers18 liked this · 8 years ago
dizzyfingers18 liked this · 8 years ago -
 lonelyaliveandtryingtobehappy reblogged this · 8 years ago
lonelyaliveandtryingtobehappy reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 aott01 liked this · 8 years ago
aott01 liked this · 8 years ago -
 iseekadventures liked this · 8 years ago
iseekadventures liked this · 8 years ago -
 rmahin liked this · 8 years ago
rmahin liked this · 8 years ago -
 busserdinda reblogged this · 8 years ago
busserdinda reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 dindabusser liked this · 8 years ago
dindabusser liked this · 8 years ago -
 aley-cat03-blog liked this · 8 years ago
aley-cat03-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 im-going-to-space liked this · 8 years ago
im-going-to-space liked this · 8 years ago -
 purified-zone reblogged this · 8 years ago
purified-zone reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 depthinfinite liked this · 8 years ago
depthinfinite liked this · 8 years ago -
 phandoms-are-here-blog liked this · 8 years ago
phandoms-are-here-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 nightmurk liked this · 8 years ago
nightmurk liked this · 8 years ago -
 the-tales-of-a-nowhere-man liked this · 8 years ago
the-tales-of-a-nowhere-man liked this · 8 years ago -
 leftistfanenboii liked this · 8 years ago
leftistfanenboii liked this · 8 years ago -
 mizukiyouko liked this · 8 years ago
mizukiyouko liked this · 8 years ago -
 edwhiteandblue liked this · 8 years ago
edwhiteandblue liked this · 8 years ago -
 under-silent-skies liked this · 8 years ago
under-silent-skies liked this · 8 years ago -
 wolfbarkbite reblogged this · 8 years ago
wolfbarkbite reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 wolfbarkbite liked this · 8 years ago
wolfbarkbite liked this · 8 years ago -
 charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago
charleshdv-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 sahu liked this · 8 years ago
sahu liked this · 8 years ago -
 yeahiamweird liked this · 8 years ago
yeahiamweird liked this · 8 years ago -
 kyriosblaze liked this · 8 years ago
kyriosblaze liked this · 8 years ago -
 knownasthegoat liked this · 8 years ago
knownasthegoat liked this · 8 years ago -
 galaxystew liked this · 8 years ago
galaxystew liked this · 8 years ago -
 stumblmer liked this · 8 years ago
stumblmer liked this · 8 years ago -
 queenailuros liked this · 8 years ago
queenailuros liked this · 8 years ago -
 qui11iam liked this · 8 years ago
qui11iam liked this · 8 years ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts








