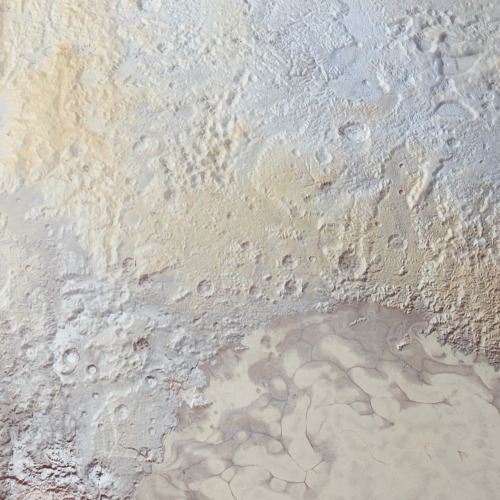
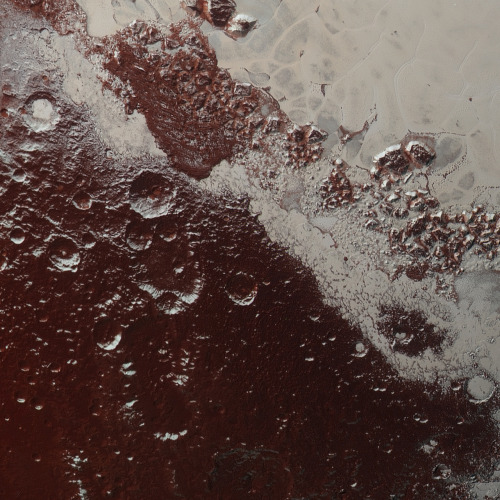
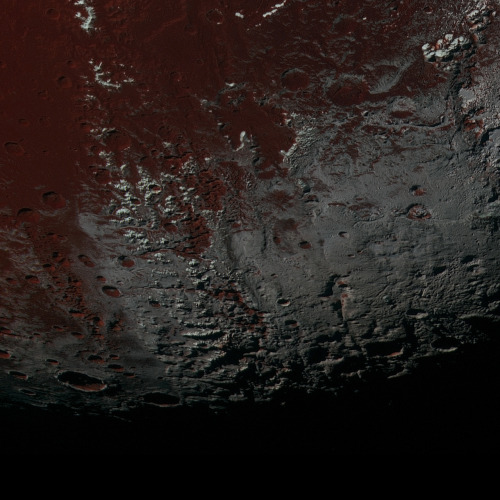
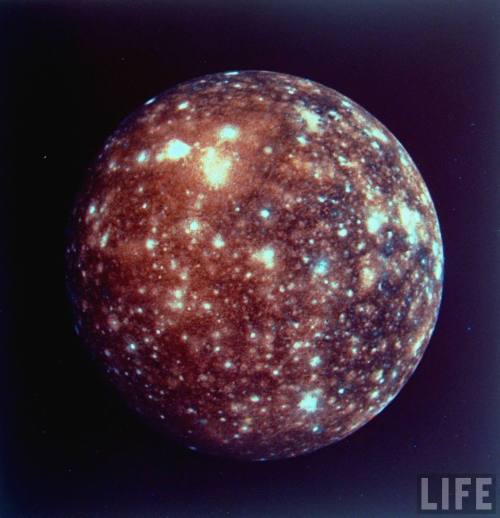
September 15
September 15
This one is technically not yet history, because at the time of posting, the little craft has about half an hour left to go. That said, let’s proceed.
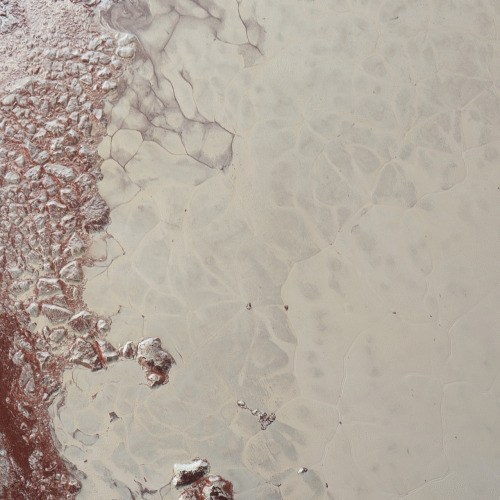
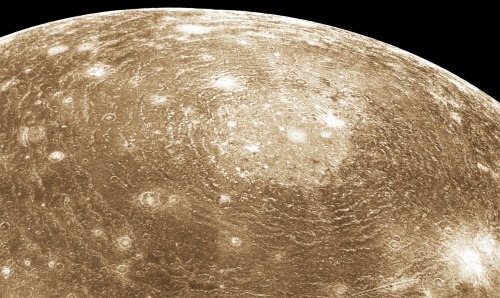
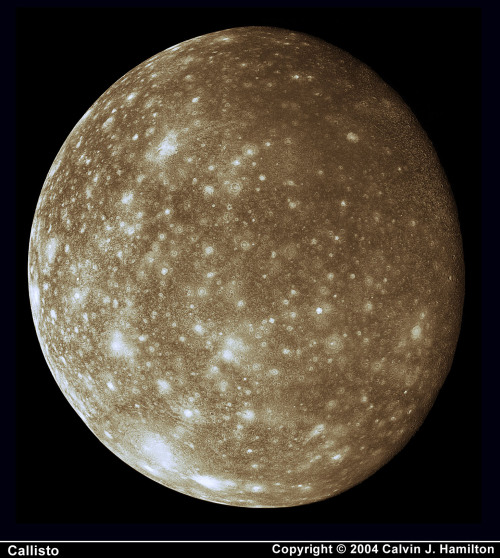
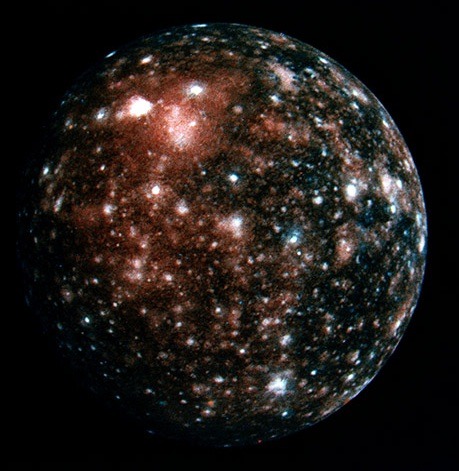
In 2017, NASA’s Cassini space probe ended its twenty-year mission at Saturn. After a nearly-seven-year-long journey there, it orbited the ringed planet for 13 years and just over two months, gathering copious amounts of information about the planet, said rings, and many of its moons. It landed an ESA probe called Huygens on Titan, the first-ever soft landing in the outer Solar System. It discovered lakes, seas, and rivers of methane on Titan, geysers of water erupting from Enceladus (and passed within 50 miles of that moon’s surface), and found gigantic, raging hurricanes at both of Saturn’s poles.
And the images it returned are beautiful enough to make you weep.
On this day in 2017, with the fuel for Cassini’s directional thrusters running low, the probe was de-orbited into the Saturnian atmosphere to prevent any possibility of any contamination of possible biotic environments on Titan or Enceladus. The remaining thruster fuel was used to keep the radio dish pointed towards Earth so the probe could transmit information about the upper atmosphere of Saturn while it was burning up due to atmospheric friction.
This is us at our best. We spent no small amount of money on a nuclear-powered robot, launched it into space, sent it a billion miles away, and worked with it for two decades just to learn about another planet. And when the repeatedly-extended missions were through, we made the little craft sacrifice itself like a samurai, performing its duty as long as it could while it became a shooting star in the Saturnian sky.

Rhea occulting Saturn

Water geysers on Enceladus

Strange Iapetus

Look at this gorgeousness

A gigantic motherfucking storm in Saturn’s northern hemisphere

Tethys

This image is from the surface of a moon of a planet at least 746 million miles away. Sweet lord

Mimas

Vertical structures in the rings. Holy shit

Titan and Dione occulting Saturn, rings visible

Little Daphnis making gravitational ripples in the rings

That’s here. That’s home. That’s all of us that ever lived.

Saturn, backlit

A polar vortex on the gas giant

Icy Enceladus
(All images from NASA/JPL)
More Posts from Fillthevoid-with-space and Others

New Zealand was lovely, but I already touched on what I’d be tempted to talk about with my Southern Stars episode. A person I interviewed as a potential new housemate gave me the idea for this episode because the joy of outer space is truly everywhere and anywhere. The field of astrogeology was not something I had heard of before, though I had indirectly heard of Eugene Shoemaker. I knew the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 was named after him (and Carolyn Shoemaker, his wife). It turns out he basically founded the modern field of astrogeology! So I talk about him for quite a while, too.
Below the cut are the glossary, transcript, sources, and music credits. Send me any topic suggestions via Tumblr message (you don’t need an account to do this, just submit as anonymous). You can also tweet at me on Twitter at @HDandtheVoid, or you can ask me to my face if you know me in real life. Subscribe on iTunes to get the new episodes of my semi-monthly podcast, and please please please rate and review it. Go ahead and tell friends if you think they’d like to hear it, too!
(The next episode is going to be famous comets, and I’m shooting for an April release.)
Glossary
aeolian processes - the wind’s ability to shape the surface of a planet by eroding, transporting, and depositing materials. Most effective in desert regions, where the sparse vegetation, dry soil, and loose sediments mean these processes have the greatest impact.
albedo features - the International Astronomical Union term for an area of a planet that has a high contrast in color with the surrounding area on a planet’s surface.
chaos terrain - the International Astronomical Union term for where ridges, cracks, and plains on a planet’s surface appear broken and smashed up against each other.
chasma - the International Astronomical Union term for a long, steep-sided, deep surface indentation in a planet’s surface.
colles - the International Astronomical Union term for collections of small, knob-like hills on the surface of a planet.
dorsum - the International Astronomical Union term for a wrinkle-like ridge on a planet’s surface.
facula - the International Astronomical Union term for a bright spot on planets or moons.
fluvial processes - the ways in which rivers and streams impact a planet’s surface by eroding or creating deposits and landforms out of sediment. Sometimes, streams or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, and then they are called glaciofluvial or fluvioglacial processes.
fossa - the International Astronomical Union term for a long, narrow depression in a planet’s surface.
lacunae - the International Astronomical Union term for irregularly shaped depressions that look like dry lake beds on the surface of Saturn’s moon, Titan.
lobate scarp - the International Astronomical Union term for a curved slope that is probably formed by compressive tectonic movement.
mare - the International Astronomical Union term for a large, circular plain on a planet’s surface.
terra - the International Astronomical Union term for an extensive landmass like a plain or highland.
tesserae - the International Astronomical Union term for regions on the planet Venus that are tiled, polygonal shapes.
vallis - the International Astronomical Union term for a valley on the surface of a planet.
Script/Transcript
Sources
Planetary geology via Wikipedia
Lunar Lobate Scarp via the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera
Eugene M. Shoemaker Biographical Memoirs via NASA
Dr. Eugene Shoemaker, 69; Set Record for Finding Comets via The New York Times (July 1997)
Eugene Shoemaker (1928-1997) via NASA Jet Propulsion Lab
Eugene Shoemaker (1928 - 1997) via American Astronomical Society
Gene Shoemaker - Founder of Astrogeology via US Geological Society
Eugene Shoemaker via the Planetary Society
Eugene Shoemaker Ashes Carried on Lunar Prospector via NASA Jet Propulsion Lab
Eugene M. Shoemaker and the Integration of Earth and Sky via GSA Today (April 2001)
Destination Moon by Carolyn C. Porco (Feb 2000)
“I wanted to include something to commemorate Gene’s scientific legacy. It seemed appropriate to choose his favorite photo of Meteor Crater and a photo of the last comet that he and his wife saw together, Comet Hale-Bopp. And somehow, I extracted from the dusty realm of dim memory a passage I had read from Romeo and Juliet long ago that seemed perfect for the occasion.”
Who is an Astrogeologist? via Space Awareness
Careers via the USGS Astrogeology Science Center
“Public Service by contributing to the public knowledge about our Solar System.”
Lunar Calibration via USGS
“The unmatched stability of the lunar surface reflectance (better than one part in 108 per year) makes the Moon attractive as a calibration light source; its radiance can be known with high precision and accuracy. The lunar irradiance is similar in brightness to sunlit land masses on the Earth.”
Video: Astrogeology 1963-2013: Fifty Years of Exploration via the USGS Astrogeology Science Center
Intro Music: ‘Better Times Will Come’ by No Luck Club off their album Prosperity
Filler Music: ‘Muddy Waters’ by LP off her album Lost On You
Outro Music: ‘Fields of Russia’ by Mutefish off their album On Draught
NASA's Swift Mission Maps a Star's 'Death Spiral' into a Black Hole
NASA - Swift Mission patch. March 20, 2017 Some 290 million years ago, a star much like the sun wandered too close to the central black hole of its galaxy. Intense tides tore the star apart, which produced an eruption of optical, ultraviolet and X-ray light that first reached Earth in 2014. Now, a team of scientists using observations from NASA’s Swift satellite have mapped out how and where these different wavelengths were produced in the event, named ASASSN-14li, as the shattered star’s debris circled the black hole. “We discovered brightness changes in X-rays that occurred about a month after similar changes were observed in visible and UV light,” said Dheeraj Pasham, an astrophysicist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and the lead researcher of the study. “We think this means the optical and UV emission arose far from the black hole, where elliptical streams of orbiting matter crashed into each other.”
Swift Charts a Star’s ‘Death Spiral’ into Black Hole
Video above: This animation illustrates how debris from a tidally disrupted star collides with itself, creating shock waves that emit ultraviolet and optical light far from the black hole. According to Swift observations of ASASSN-14li, these clumps took about a month to fall back to the black hole, where they produced changes in the X-ray emission that correlated with the earlier UV and optical changes. Video Credits: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. Astronomers think ASASSN-14li was produced when a sun-like star wandered too close to a 3-million-solar-mass black hole similar to the one at the center of our own galaxy. For comparison, the event horizon of a black hole like this is about 13 times bigger than the sun, and the accretion disk formed by the disrupted star could extend to more than twice Earth’s distance from the sun. When a star passes too close to a black hole with 10,000 or more times the sun’s mass, tidal forces outstrip the star’s own gravity, converting the star into a stream of debris. Astronomers call this a tidal disruption event. Matter falling toward a black hole collects into a spinning accretion disk, where it becomes compressed and heated before eventually spilling over the black hole’s event horizon, the point beyond which nothing can escape and astronomers cannot observe. Tidal disruption flares carry important information about how this debris initially settles into an accretion disk. Astronomers know the X-ray emission in these flares arises very close to the black hole. But the location of optical and UV light was unclear, even puzzling. In some of the best-studied events, this emission seems to be located much farther than where the black hole’s tides could shatter the star. Additionally, the gas emitting the light seemed to remain at steady temperatures for much longer than expected. ASASSN-14li was discovered Nov. 22, 2014, in images obtained by the All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASASSN), which includes robotic telescopes in Hawaii and Chile. Follow-up observations with Swift’s X-ray and Ultraviolet/Optical telescopes began eight days later and continued every few days for the next nine months. The researchers supplemented later Swift observations with optical data from the Las Cumbres Observatory headquartered in Goleta, California.
Image above: This artist’s rendering shows the tidal disruption event named ASASSN-14li, where a star wandering too close to a 3-million-solar-mass black hole was torn apart. The debris gathered into an accretion disk around the black hole. New data from NASA’s Swift satellite show that the initial formation of the disk was shaped by interactions among incoming and outgoing streams of tidal debris. Image Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. In a paper describing the results published March 15 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Pasham, Cenko and their colleagues show how interactions among the infalling debris could create the observed optical and UV emission. Tidal debris initially falls toward the black hole but overshoots, arcing back out along elliptical orbits and eventually colliding with the incoming stream. “Returning clumps of debris strike the incoming stream, which results in shock waves that emit visible and ultraviolet light,” said Goddard’s Bradley Cenko, the acting Swift principal investigator and a member of the science team. “As these clumps fall down to the black hole, they also modulate the X-ray emission there.”
Swift spacecraft. Image Credit: NASA
Future observations of other tidal disruption events will be needed to further clarify the origin of optical and ultraviolet light. Goddard manages the Swift mission in collaboration with Pennsylvania State University in University Park, the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico and Orbital Sciences Corp. in Dulles, Virginia. Other partners include the University of Leicester and Mullard Space Science Laboratory in the United Kingdom, Brera Observatory and the Italian Space Agency in Italy, with additional collaborators in Germany and Japan. Related: Scientists Identify a Black Hole Choking on Stardust (MIT): http://news.mit.edu/2017/black-hole-choking-stardust-0315 ASASSN-14li: Destroyed Star Rains onto Black Hole, Winds Blow it Back: http://chandra.harvard.edu/photo/2015/tidal/ 'Cry’ of a Shredded Star Heralds a New Era for Testing Relativity: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/swift/bursts/shredded-star.html Researchers Detail How a Distant Black Hole Devoured a Star: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/swift/bursts/devoured-star.html All Sky Automated Survey for SuperNovae (ASASSN): http://www.astronomy.ohio-state.edu/~assassin/index.shtml Las Cumbres Observatory: https://lco.global/ NASA’s Swift: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/swift/main/index.html Images (mentioned), Video (mentioned), Text, Credits: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, by Francis Reddy/Karl Hille. Greetings, Orbiter.ch Full article

Haaaaaay I’m on iTunes now! Slightly more convenient to download maybe!
Five Famous Pulsars from the Past 50 Years
Early astronomers faced an obstacle: their technology. These great minds only had access to telescopes that revealed celestial bodies shining in visible light. Later, with the development of new detectors, scientists opened their eyes to other types of light like radio waves and X-rays. They realized cosmic objects look very different when viewed in these additional wavelengths. Pulsars — rapidly spinning stellar corpses that appear to pulse at us — are a perfect example.

The first pulsar was observed 50 years ago on August 6, 1967, using radio waves, but since then we have studied them in nearly all wavelengths of light, including X-rays and gamma rays.
Typical Pulsar
Most pulsars form when a star — between 8 and 20 times the mass of our sun — runs out of fuel and its core collapses into a super dense and compact object: a neutron star.

These neutron stars are about the size of a city and can rotate slowly or quite quickly, spinning anywhere from once every few hours to hundreds of times per second. As they whirl, they emit beams of light that appear to blink at us from space.
First Pulsar
One day five decades ago, a graduate student at the University of Cambridge, England, named Jocelyn Bell was poring over the data from her radio telescope - 120 meters of paper recordings.

Image Credit: Sumit Sijher
She noticed some unusual markings, which she called “scruff,” indicating a mysterious object (simulated above) that flashed without fail every 1.33730 seconds. This was the very first pulsar discovered, known today as PSR B1919+21.
Best Known Pulsar
Before long, we realized pulsars were far more complicated than first meets the eye — they produce many kinds of light, not only radio waves. Take our galaxy’s Crab Nebula, just 6,500 light years away and somewhat of a local celebrity. It formed after a supernova explosion, which crushed the parent star’s core into a neutron star.

The resulting pulsar, nestled inside the nebula that resulted from the supernova explosion, is among the most well-studied objects in our cosmos. It’s pictured above in X-ray light, but it shines across almost the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to gamma rays.
Brightest Gamma-ray Pulsar
Speaking of gamma rays, in 2015 our Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope discovered the first pulsar beyond our own galaxy capable of producing such high-energy emissions.

Located in the Tarantula Nebula 163,000 light-years away, PSR J0540-6919 gleams nearly 20 times brighter in gamma-rays than the pulsar embedded in the Crab Nebula.
Dual Personality Pulsar
No two pulsars are exactly alike, and in 2013 an especially fast-spinning one had an identity crisis. A fleet of orbiting X-ray telescopes, including our Swift and Chandra observatories, caught IGR J18245-2452 as it alternated between generating X-rays and radio waves.

Scientists suspect these radical changes could be due to the rise and fall of gas streaming onto the pulsar from its companion star.
Transformer Pulsar
This just goes to show that pulsars are easily influenced by their surroundings. That same year, our Fermi Gamma Ray Space Telescope uncovered another pulsar, PSR J1023+0038, in the act of a major transformation — also under the influence of its nearby companion star.

The radio beacon disappeared and the pulsar brightened fivefold in gamma rays, as if someone had flipped a switch to increase the energy of the system.
NICER Mission
Our Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) mission, launched this past June, will study pulsars like those above using X-ray measurements.

With NICER’s help, scientists will be able to gaze even deeper into the cores of these dense and mysterious entities.
For more information about NICER, visit https://www.nasa.gov/nicer
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
I still highly recommend this good, beautiful web comic about love in space, and now it's all done! You can read it all.




The final three chapters are up. Read it now.
That’s it folks, On A Sunbeam is over. Though I am pondering a sequel.
Thank you all so much for following along.
I saw the picture and I thought it was a photo of the space between a Venetian blind and a window frame but no. No. It was a moon between the rings of Saturn.
The world's oldest story? Astronomers say global myths about 'seven sisters' stars may reach back 100,000 years https://phys.org/news/2020-12-world-oldest-story-astronomers-global.html

Holy shit, this is cool!
So many cultures call the Pleiades some variation of the "seven sisters" despite only having six visible stars. There only appear to be six because two of the stars are so close together as to appear as one.
The myths also mention one sister leaving or hiding to explain why there's only six. And based off observations and measurements, those two that are so close together used to be visibly separate. One literally has moved to hide.
And based off the similarities between the more commonly known Greek myth and the Aboriginal Australian myth, plus some other stuff, this myth could possibly even date back to when humanity still all resided in Africa!

Oh my gosh this is incredibly exciting! Imagine combining them with a Star Wars LEGO set...
-
 annita89v5a8zjh liked this · 6 months ago
annita89v5a8zjh liked this · 6 months ago -
 ohbarf reblogged this · 8 months ago
ohbarf reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 ohbarf liked this · 8 months ago
ohbarf liked this · 8 months ago -
 likeaduck liked this · 8 months ago
likeaduck liked this · 8 months ago -
 nikkifromtabs reblogged this · 8 months ago
nikkifromtabs reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 incorrigibly---frivolous reblogged this · 8 months ago
incorrigibly---frivolous reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 arcaneaccount liked this · 8 months ago
arcaneaccount liked this · 8 months ago -
 thriron reblogged this · 8 months ago
thriron reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 thriron liked this · 8 months ago
thriron liked this · 8 months ago -
 dream-in-blue liked this · 8 months ago
dream-in-blue liked this · 8 months ago -
 jubileegeode liked this · 8 months ago
jubileegeode liked this · 8 months ago -
 vulpes-aestatis reblogged this · 8 months ago
vulpes-aestatis reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 againstadarkbackground liked this · 8 months ago
againstadarkbackground liked this · 8 months ago -
 againstadarkbackground reblogged this · 8 months ago
againstadarkbackground reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 dolby-5 reblogged this · 1 year ago
dolby-5 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 virtualfishcashbonk liked this · 1 year ago
virtualfishcashbonk liked this · 1 year ago -
 future-ex-mr-malcolm reblogged this · 1 year ago
future-ex-mr-malcolm reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yeoldbarback reblogged this · 1 year ago
yeoldbarback reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yeoldbarback reblogged this · 1 year ago
yeoldbarback reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 yeoldbarback liked this · 1 year ago
yeoldbarback liked this · 1 year ago -
 jaco-paatorios-bass-fkshing reblogged this · 1 year ago
jaco-paatorios-bass-fkshing reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 eldritchsage reblogged this · 1 year ago
eldritchsage reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 eldritchsage liked this · 1 year ago
eldritchsage liked this · 1 year ago -
 pepercress liked this · 1 year ago
pepercress liked this · 1 year ago -
 tolookbeyondtheglory liked this · 1 year ago
tolookbeyondtheglory liked this · 1 year ago -
 tylleet liked this · 1 year ago
tylleet liked this · 1 year ago -
 gmd reblogged this · 1 year ago
gmd reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 gmd reblogged this · 1 year ago
gmd reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 bloodmammoth reblogged this · 1 year ago
bloodmammoth reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 michaeldirnt liked this · 1 year ago
michaeldirnt liked this · 1 year ago -
 helenorvana reblogged this · 1 year ago
helenorvana reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 crazy-purple-kitten liked this · 1 year ago
crazy-purple-kitten liked this · 1 year ago -
 froggjsh22 reblogged this · 1 year ago
froggjsh22 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 froggjsh22 liked this · 1 year ago
froggjsh22 liked this · 1 year ago -
 elyserie reblogged this · 1 year ago
elyserie reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sandrajonesposts liked this · 1 year ago
sandrajonesposts liked this · 1 year ago -
 friendlyneighborhoodmenace reblogged this · 1 year ago
friendlyneighborhoodmenace reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 friendlyneighborhoodmenace liked this · 1 year ago
friendlyneighborhoodmenace liked this · 1 year ago -
 paintedtiger reblogged this · 1 year ago
paintedtiger reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 derpypandaqueen reblogged this · 1 year ago
derpypandaqueen reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 derpypandaqueen liked this · 1 year ago
derpypandaqueen liked this · 1 year ago -
 poblachtnahoibrithe liked this · 1 year ago
poblachtnahoibrithe liked this · 1 year ago -
 waveformtheta reblogged this · 1 year ago
waveformtheta reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sugarforsalt liked this · 1 year ago
sugarforsalt liked this · 1 year ago -
 elodiedreams reblogged this · 1 year ago
elodiedreams reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 elodiedreams liked this · 1 year ago
elodiedreams liked this · 1 year ago -
 dadnerdrants reblogged this · 1 year ago
dadnerdrants reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 jron reblogged this · 1 year ago
jron reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 jron liked this · 1 year ago
jron liked this · 1 year ago
A podcast project to fill the space in my heart and my time that used to be filled with academic research. In 2018, that space gets filled with... MORE SPACE! Cheerfully researched, painstakingly edited, informal as hell, definitely worth everyone's time.
243 posts