Sean Bienvenidos, Japonistasarqueológicos A Una Nueva Entrega, En Esta Ocasión Hablaré Sobre Actualidad





Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos a una nueva entrega, en esta ocasión hablaré sobre actualidad nipona, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. — El domingo 16 de julio, azotaron fuertes lluvias al archipiélago nipón y hace no mucho el tifón Lan paralizó el tráfico aéreo de Japón y dejó miles de evacuados al oeste, además sin electricidad. Pero en este caso se han anegado muchas zonas del norte, causando efectos geográficos catastróficos y causando evacuaciones, etc. Por ejemplo: La ciudad de Akita registró precipitaciones, fue un récord, más de 250 milímetros durante un período de 48 horas, todo un hito histórico. — Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana. - Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment, this time I will be talking about Japanese current affairs, and once that is said, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - On Sunday 16th July, heavy rains hit the Japanese archipelago and not long ago Typhoon Lan paralysed Japan's air traffic and left thousands of evacuees in the west without electricity. But in this case many areas in the north have been flooded, causing catastrophic geographical effects and causing evacuations, etc. For example: The city of Akita recorded record rainfall of more than 250 millimetres over a 48-hour period, a historic milestone. - I hope you like it and see you in future posts, have a good week. - 日本の考古学者たちよ、新しい回へようこそ。今回は日本の時事問題についてお話しします。そう言ったら、くつろいで、始めましょう。 - 7月16日の日曜日、日本列島は大雨に見舞われ、少し前には台風12号が日本の空の便を麻痺させ、西日本では何千人もの避難者が停電に見舞われた。しかし今回は、北部の多くの地域が浸水し、地理的に壊滅的な影響を引き起こし、避難などを余儀なくされている。例えば:秋田市では、48時間に250ミリ以上の記録的な雨量を記録し、歴史的な出来事となった。 - お気に召していただけたなら幸いである.
More Posts from Noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas and Others





Sean bienvenidos japonsistasarqueológicos, a una nueva entrega cultural en esta ocasión os voy comentar la festividad, del día del niño que se celebra cada 5 de Mayo que se llama Kodomo no Hi y se escribiríaこどもの日 una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - ¿Cuándo surgió el día del niño?La festividad, surge en el siglo VIII d.c en lo que respondería al periodo Heian, posiblemente tendría influencia de china al respecto ya que se basó en Tango no Sekku. El Sekku se basa en los puntos de inflexión de las estaciones y se basa en la teoría de los cinco elementos del yin y el yang en China. - La forma tradicional de celebrarlo es ofrecer ofrendas estacionales a los dioses, rezar y comer juntos los productos de segunda mano.En el período Kamakura, en pleno auge de los samurais, se convirtió en un evento importante para orar por el crecimiento y la salud de los niños y la prosperidad de la familia, con adornos como armaduras, cascos, serpentinas de carpa y muñecos festivos. - Ahora a continuación mencionaré algunos dulces de los que se suelen comer el 5 de Mayo: Kashiwa mochi,Chimaki, beko mochi, akumaki , pastel no koi. - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones y que pasen un feliz día del niño.
-
今回は、毎年5月5日に行われる「こどもの日」というお祭りについてお話しします。「こどもの日」とは、「こどもの日」と書いて「こどもの日」と読みます。 - こどもの日」の起源は、紀元8世紀の平安時代にさかのぼりますが、「端午の節句」が元になっていることから、中国の影響を受けている可能性があります。節句とは、季節の変わり目を表すもので、中国の陰陽五行説に基づくものです。 - 季節のお供え物を神に捧げ、祈り、中古品をみんなで食べるのが伝統的な祝い方です。 武士ブーム真っ只中の鎌倉時代には、甲冑や兜、こいのぼり、祝い人形などを飾り、子供の成長や健康、家族の繁栄を祈る大切な行事となりました。 - 柏餅、ちまき、べこ餅、あくまき、こいのぼりのお菓子です。 - 気に入っていただけたなら幸いです。今後の記事でお会いしましょう。そして、楽しい子供の日をお過ごしください。
-
Welcome to a new cultural delivery in this occasion I am going to comment on the festivity, the day of the child that is celebrated every 5th of May that is called Kodomo no Hi and it would be writtenこどもの日 once said this make yourselves comfortable that we begin. - When did Children's Day come about? The holiday, which dates back to the 8th century AD in what would be the Heian period, was possibly influenced by Chinese in this respect as it was based on Tango no Sekku. Sekku is based on the turning points of the seasons and is based on the five element theory of yin and yang in China. - The traditional way to celebrate it is to offer seasonal offerings to the gods, pray and eat second-hand goods together. In the Kamakura period, at the height of the samurai boom, it became an important event to pray for the growth and health of children and the prosperity of the family, with decorations such as armour, helmets, carp streamers and festive dolls. - Now here are some of the sweets usually eaten on May 5th: Kashiwa mochi, Chimaki, beko mochi, akumaki, no koi cake. - I hope you liked it and see you in future posts and have a happy children's day.






Sean bienvenidos japonistasarqueológicos a una nueva entrega en esta ocasión os hablaré sobre Cryptomeria japonica (スギ), más popularmente conocido como el cedro japonés, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - Se localizan al sur de Hokkaido (ほっかいどう) el cedro es el árbol más alto de Japón, y los árboles más altos superan los 50 m. Además son los árboles más longevos de Japón,hay árboles que tienen entre 2000 y 3000 años en todo Japón. - Espero que os guste ¿lo conocían? os deseo una feliz semana y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones del país del sol naciente. - 今回は、杉の木(Cryptomeria japonica, スギ)についてのお話です。 - 北海道の南に位置するスギは、日本で最も高い木で、高い木は50mを超えます。また、日本で最も長寿の木でもあり、日本各地に樹齢2000年から3000年の木があるそうです。 - それでは、今週も一週間、どうぞよろしくお願いいたします。 - Welcome japonistasarqueológicos to a new installment in this occasion I will talk about Cryptomeria japonica (スギ), more popularly known as the Japanese cedar, having said that, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - Located south of Hokkaido (ほっかいどう) the cedar is the tallest tree in Japan, with the tallest trees exceeding 50m. They are also the longest-lived trees in Japan,there are trees that are between 2000 and 3000 years old all over Japan. - I hope you like it, did you know it? I wish you a happy week and see you in future publications from the land of the rising sun.








Chapter 2: Pre-Jomon Japan Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new archaeological installment. Having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's begin. - In the previous publication we made a short description, commenting on where the Kasuke neighborhood of the city of Midori is located, Gunma prefecture in the northern region of Kantō, we also commented on when the Upper Paleolithic dates back to 35,000 / 25,000 BC. Currently the Iwajuku III culture is 40,000 and possibly even older, only future research will shed more light on this culture and the Japanese passage, its discoverer was Tadahiro Aizawa, during the 1946 showa era of post-war Japan, excavation has continued until our present that corresponds to the Heisei era. - I hope you liked it and see you in future posts, have a good week. 第2章: 縄文以前の日本 日本の考古学者の皆さん、新しい考古学へようこそ。そうは言っても、気を楽にして始めましょう。 - 前回の出版物では、関東北部の群馬県みどり市の嘉助地区がどこにあるかについて簡単な説明を行い、上部旧石器時代がいつ紀元前 35,000 年 / 25,000 年に遡るかについてもコメントしました。現在、岩宿Ⅲ文化は 40,000 個あり、おそらくさらに古いものである可能性があります。この文化と日本語の歴史にさらに光を当てるのは将来の研究だけです。その発見者は相沢忠宏で、戦後日本の 1946 年の昭和時代に、発掘は現在まで続けられています。それは平成に相当します。 - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の投稿でお会いしましょう。良い一週間をお過ごしください。 - Capítulo 2: El japón pre-Jomon Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologos, a una nueva entrega, arqueológica, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - En la publicación anterior hicimos una pequeña descripción, comentando donde se localiza el barrio de Kasuke de la ciudad de Midori, prefectura de Gunma en la región norte de Kantō, también comentamos de cuando data paleolítico superior 35.000 / 25000 a.c. Actualmente la cultura Iwajuku III y es de 40.000 e incluso más antigua posiblemente, únicamente futuras investigaciones arrojará más luz sobre esta cultura y el pasadizo japonés, su descubridor fue Tadahiro Aizawa, durante la era showa 1946 del Japón de la posguerra, se ha seguido excavando hasta nuestro presente que corresponde a la era Heisei. - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana.









Capítulo 1: INTRODUCCIÓN El japón pre-Jomon. Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologos, a una nueva entrega, arqueológica, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - En esta ocasión nos trasladamos al yacimiento arqueológico Iwajuku, es un sitio arqueológico que está ubicado en lo que ahora corresponde al barrio de Kasuke en la ciudad de Midori, prefectura de Gunma en la región de Kantō, este lugar recibió protección como Sitio Histórico Nacional en 1979 por parte de la unesco y data del paleolítico superior 35.000 -25000 a.C mucho más antiguo que el periodo Jomon estudios recientes lo fechan hace 40.000 años. Las fotos que os mostraré a continuación son del museo de la universidad Meiji, aparte de industria lítica hecha con obsidiana también hay guijarros de piedra. - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana. Capítulo 1: INTRODUCCIÓN El japón pre-Jomon. Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologos, a una nueva entrega, arqueológica, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - En esta ocasión nos trasladamos al yacimiento arqueológico Iwajuku, es un sitio arqueológico que está ubicado en lo que ahora corresponde al barrio de Kasuke en la ciudad de Midori, prefectura de Gunma en la región de Kantō, este lugar recibió protección como Sitio Histórico Nacional en 1979 por parte de la unesco y data del paleolítico superior 35.000 -25000 a.C mucho más antiguo que el periodo Jomon estudios recientes lo fechan hace 40.000 años. Las fotos que os mostraré a continuación son del museo de la universidad Meiji, aparte de industria lítica hecha con obsidiana también hay guijarros de piedra. - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana. - 第 1 章: はじめに 縄文以前の日本。 日本の考古学者の皆さん、新しい考古学へようこそ。そうは言っても、気を楽にして始めましょう。 - この度、岩宿遺跡へ移動しました。 岩宿遺跡は、現在の関東地方の群馬県みどり市嘉助地区に相当する遺跡で、平成29年に国の史跡として保護されています。 1979年にユネスコによって認定され、その起源は紀元前3万5千年から紀元前2万5千年の後期旧石器時代にまで遡り、縄文時代よりはるかに古く、最近の研究では4万年前のものであると推定されています。以下に紹介する写真は明治大学博物館所蔵のものですが、黒曜石を使った石工業のほかに石の小石もあります。 - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の投稿でお会いしましょう。良い一週間をお過ごしください。 - Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION Pre-Jomon Japan. Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new archaeological installment. Having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's begin. - On this occasion we moved to the Iwajuku archaeological site, it is an archaeological site that is located in what now corresponds to the Kasuke neighborhood in the city of Midori, Gunma prefecture in the Kantō region, this place received protection as a National Historic Site in 1979 by UNESCO and dates back to the Upper Paleolithic 35,000 / 25,000 BC, much older than the Jomon period, recent studies date it to 40,000 years ago. The photos that I will show you below are from the Meiji University Museum, apart from lithic industry made with obsidian there are also stone pebbles. - I hope you liked it and see you in future posts, have a good week.

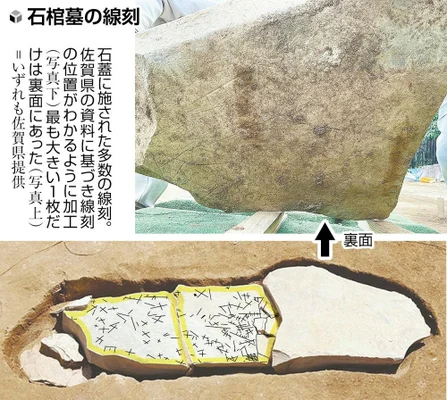



Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos, a una nueva entrega de arqueología nipona, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos qué empezamos. - Nos volvemos a trasladar a la prehistoria japonesa que, cada día, nos sorprende con un nuevo hallazgo arqueológico. Las ruinas de Yoshinogari, datan del periodo Yayoi, pero en este caso del Yayoi tardio y se localizan en la prefectura de saga. - Se trata de una tumba de unos dos metros de largo¿Quién estaba enterrado en ella? Futuras investigaciones arrojarán luz. ¿Qué opinan ustedes sobre este hallazgo? - Os deseo una feliz semana y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones. 日本の考古学者たちよ、ようこそ!それでは、くつろいでいただき、始めましょう。 - 毎日、新しい考古学的発見で私たちを驚かせてくれる日本の先史時代へと話を戻します。吉野ヶ里遺跡は、佐賀県にある弥生時代後期の遺跡です。 - 古墳の長さは約2メートル。 誰が埋葬されていたのだろうか。この発見は、今後の研究によって明らかにされるでしょう。 あなたはどう思われますか? - それでは、今週もよろしくお願いします。また、今後の記事でお会いしましょう。 - Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new instalment of Japanese archaeology, so make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - We move back to Japanese prehistory, which surprises us every day with a new archaeological find. The ruins of Yoshinogari, dating back to the Yayoi period, but in this case to the late Yayoi period, are located in the prefecture of Saga. - The tomb is about two metres long. Who was buried in it? Further research will shed light on this discovery. What do you think about it? - I wish you a happy week and see you in future posts.

日本の考古学と科学思想の歴史。
第2章 :
日本の考古学者の皆さん、哲学的観点から見た新しい日本考古学へようこそ。 — 前の章で、特定のトピック、歴史、考古学、人類学について質問されるとき、たとえば「私たちの先祖は誰ですか?」とコメントしました。 そして彼らはどうやって X 場所にたどり着いたのでしょうか? 考古学自体が 19 世紀末の 1877 年に登場したとき、1884 年に人類学研究所が、1895 年に日本考古学協会が誕生したことについて触れます。 - 19 世紀の人なら、「私は誰ですか、どこから来たのですか?」と尋ねるでしょう。 ドイツ語、中国語、ノルウェー語、日本語などを尋ねることができます。 この種の質問は今日に至るまで答えられていません。 歴史学と考古学はそれらに答えを与えておらず、今日の他の分野でさえさらに多くのことを知っていますが、道のりはまだ長いです。 19世紀の日本、特にその終わり頃は、自分たちの起源を知りませんでした。 1980 年代の日本の科学者なら誰でも、最初の日本人入植者は誰だったのか疑問に思うでしょう。 ここに定住するきっかけは何ですか? 現在、最初の入植者は約 3 万年前に到着したことが知られていますが、彼らだけだったのでしょうか? この諸島には、海面が現在より 120 倍も低かったため、中国と朝鮮の半島を北と南から通ってやって来た最初の入植者がいたことが知られています。 日本人は非常に古い本を 2 冊持っていることが知られており、1 冊は西暦 711 年、もう 1 冊は西暦 722 年のものです。 最初の書紀は古事記と呼ばれ、二番目の日本書紀は、神 (カミスと呼ばれる) による西暦 660 年からの日本の建国について語っています。この日本の神聖な起源の概念は、第二次世界大戦 (第二次世界大戦) まで続きます。 これら 2 冊の本は、ヨーロッパではギリシャとローマに遡る最古の本に相当します。 - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の投稿でお会いしましょう。良い一週間をお過ごしください。
HISTORY OF JAPANESE ARCHEOLOGY AND SCIENTIFIC THOUGHT.
Episode 2:
Welcome, Japanesearchaeologicalists, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, seen from a philosophical point of view. Having said that, get comfortable and let's begin.
—
In the previous chapter, we commented that when we are asked questions about certain topics, history, archeology and anthropology, for example: Who were our ancestors? And how did they get to X place? We mention, when archeology itself emerged at the end of the 19th century, 1877, the origin of the anthropology laboratory in 1884 and in 1895 the Japanese archeology society.
-
A person from the 19th century would ask: Who am I, where do I come from? We could ask a: German, Chinese, Norwegian, Japanese, etc. These types of questions remain unanswered to this day. History and archeology have not given them an answer, even other disciplines today know much more, but there is still a long way to go. Japan during the 19th century, especially the end of that period, did not know its own origin. Any Japanese scientist in the 1980s would wonder who were the first Japanese settlers? What led you to settle here? Currently, it is known that the first settlers arrived about 30,000 years ago. Were they the only ones? It is known that the archipelago was inhabited by other inhabitants who were the first settlers. They arrived through the peninsula of China and Korea, both from the north and the south, since the sea level was 120 times lower than today. It is known that the Japanese have two very old books, one dates from 711 and the other from 722 AD. The first is called Kojiki and the second Nihonshoki, the Kojiki tells of the founding of Japan from the year 660 AD by the gods (called kamis), this concept of the divine origin of Japan would last until World War II (2ww). These two books would be the equivalent in Europe of the oldest dating back to Greece and Rome.
-
I hope you liked it and see you in future posts, have a good week.


Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos, a una nueva entrega de religión nipona, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos qué empezamos. - Seguramente, todos hemos escuchado hablar del Budismo y Sintoísmo, dos religiones muy diferentes entre sí, ya que sus pilares religiosos no están hechos de la misma materia, voy a intentar resumir este tema para que todos podamos entenderlo mejor. ¿Cuándo llego el budismo a Japón? Llego en el siglo VI d.c en el período kofun también denominado protohistoria, lo que no voy a negar y lo que todos sabemos es que china, India y otros países influenciaron a Japón y eso lo podemos ver todavía a día de hoy. - Pero hace poco vi el uso de la palabra Sincretismo religioso, lo cual, me parece el término de lo menos apropiado, ¿Qué significa sincretismo? Unión, fusión e hibridación, casos más claros, lo podemos ver en Latinoamérica y con Grecia y Roma. Por lo cual el término más apropiado para este caso sería coexistencia o convivencia, además en el periodo meiji hubo una reforma religiosa para separar ambas religiones y convivencia al sintoísmo, religión del estado, a esto se le llama Shinbutsu bunri en hiragana sería:(しんぶつぶんり) ¿Qué opinan ustedes? - Espero que os haya gustado y nos veamos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana. - Primera foto :santuario Heian Jingu(Kyoto) Segunda foto: Templo Rengeoin( Kyoto) - Welcome, archaeological Japanists, to a new installment of Japanese religion, having said that, make yourself comfortable as we begin. - Surely, we have all heard of Buddhism and Shintoism, two very different religions from each other, since their religious pillars are not made of the same material, I am going to try to summarize this topic so that we can all understand it better. When did Buddhism arrive in Japan? It arrived in the 6th century AD in the Kofun period also called protohistory, which I will not deny and what we all know is that China, India and other countries influenced Japan and we can still see that today. - But I recently saw the use of the word religious syncretism, which seems to me to be the least appropriate term. What does syncretism mean? Union, fusion and hybridization, clearest cases, we can see it in Latin America and with Greece and Rome. Therefore, the most appropriate term for this case would be coexistence or coexistence. In addition, in the Meiji period there was a religious reform to separate both religions and coexistence with Shintoism, the state religion. This is called Shinbutsu bunri in hiragana: (しん ぶつぶんり) What do you think? - I hope you liked it and we'll see you in future posts and have a good week. - First photo: Heian Jingu Shrine (Kyoto) Second photo: Rengeoin Temple (Kyoto) - 考古学者の日本主義者の皆さん、日本の宗教の新しい記事へようこそ。そうは言っても、安心して始めてください。 - 確かに、私たちは皆、仏教と神道という、互いにまったく異なる 2 つの宗教について聞いたことがあるでしょう。それらの宗教的支柱は同じ素材で作られていないため、私たち全員がよりよく理解できるように、このトピックを要約してみようと思います。 仏教はいつ日本に伝わったのでしょうか? それは、原史時代とも呼ばれる古墳時代の西暦 6 世紀に到来しました。私はそれを否定しません。また、中国、インド、その他の国々が日本に影響を与えたことは誰もが知っており、今日でもそれを見ることができます。 - しかし、私は最近、宗教的混合主義という言葉が使われているのを目にしましたが、これは私にとって最も不適切な用語であるように思えます。 結合、融合、ハイブリッド化の最も明確な事例は、ラテンアメリカやギリシャ、ローマで見られます。 したがって、この場合には「共存」または「共生」という言葉が最も適切でしょう。また、明治時代には両宗教を分離し、国教である神道と共存する宗教改革が行われました。これをひらがなで「神仏分理」といいます。ぶつぶんり)どう思いますか? - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の投稿でお会いしましょう。良い一週間をお過ごしください。 - 1枚目の写真:平安神宮(京都) 写真2枚目:蓮華王院(京都)



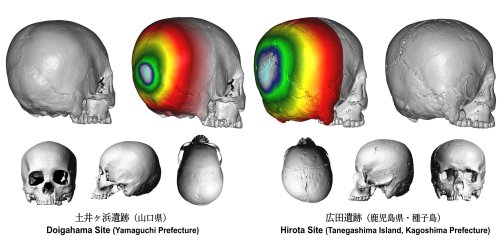
Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos, a una nueva entrega de arqueología nipona, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos qué empezamos. - En esta ocasión vamos a hablar, de cómo se deformaba el cráneo de forma antropogénica en el sitio arqueológico de Hirota en Tanegashima, localizado en la prefectura de Kagoshima. El yacimiento data del periodo yayoi 400 al 250 d.c - La deformación craneal ya se daba en muchas culturas de América, con motivos religiosos y sociales y posiblemente aquí podremos hallar el mismo caso similar o parecido, al ser un hallazgo reciente todavía faltan muchos estudios para ello. ¿Qué opinan ustedes al respecto? ¿Conocían este lugar? - En el caso de las culturas Americanas, le ponían cuerdas para alargar el cráneo¿Practicaban las mismas actividades? Quien sabe lo que nos depara el futuro, esta publicación está hecha con intenciones científica-divulgativa para transmitir conocimiento al mundo. - Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana.
-
Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's start.
-
On this occasion we are going to talk about how the skull was deformed in an anthropogenic way in the archaeological site of Hirota in Tanegashima, located in the Kagoshima prefecture. The site dates from the Yayoi period 400 to 250 AD
-
Cranial deformation already occurred in many cultures in America, for religious and social reasons and possibly here we can find the same or similar case, as it is a recent finding, many studies are still missing for it. What do you think about it? Did you know this place? - In the case of American cultures, they used ropes to lengthen the skull. Did they practice the same activities? Who knows what the future holds for us, this publication is made with scientific-informative intentions to transmit knowledge to the world. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a good week.Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's start.
-
On this occasion we are going to talk about how the skull was deformed in an anthropogenic way in the archaeological site of Hirota in Tanegashima, located in the Kagoshima prefecture. The site dates from the Yayoi period 400 to 250 AD
-
Cranial deformation already occurred in many cultures in America, for religious and social reasons and possibly here we can find the same or similar case, as it is a recent finding, many studies are still missing for it. What do you think about it? Did you know this place?
-
In the case of American cultures, they used ropes to lengthen the skull. Did they practice the same activities? Who knows what the future holds for us, this publication is made with scientific-informative intentions to transmit knowledge to the world. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a good week.
-
日本の考古学者の皆さん、日本の考古学の新しい記事へようこそ。そうは言っても、気を楽にして始めましょう。
-
今回は、鹿児島県種子島の広田遺跡で、人為的に頭蓋骨がどのように変形されたのかについてお話します。この遺跡は、弥生時代、西暦 400 年から 250 年に遡ります。 頭蓋骨の変形は、宗教的および社会的理由により、アメリカの多くの文化ですでに発生しており、おそらくここでも同じまたは類似の症例が見つかる可能性があります。これは最近の発見であるため、多くの研究がまだ不足しています。あなたはそれについてどう思いますか?この場所を知っていましたか? - アメリカ文化の場合、頭蓋骨を伸ばすためにロープを使用していましたが、同じ活動を行っていたのでしょうか?私たちの将来がどうなるかは誰にもわかりませんが、この出版物は、知識を世界に伝えるという科学的有益な意図を持って作成されています。
-
気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の出版物でお会いできることを願っています。良い一週間をお過ごしください




Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologicos a una nueva entrega en la que hablaremos sobre el asunto de Japón y las aguas residuales al mar una vez dicho esto pongan cómodos que empezamos. - Hace poco están en todos los medios de comunicación del mundo, que Japón tiene luz verde por la ONU para verter agua tratada en la planta nuclear de Fukushima en el accidente acontecido en 2011. - Hay más de 1.000 tanques y 1,34 millones de toneladas, posiblemente al 98% de la capacidad, además se está analizando el agua de mar y los alrededores de la central nuclear, actualmente se está analizando la concentración de tritio, los resultados estarán disponibles el día 25 por la tarde, previamente se habían tomado muestras de agua de los depósitos dando como resultado que era seguro, pero posiblemente tendrían que haber esperado más tiempo. - La población japonesa, se manifiesta al respecto porque esto va a generar problemas a largo plazo a la economía mundial. China suspende todas las importaciones de productos del mar japoneses, no se iba a quedar de brazos cruzados ¿Qué opinan ustedes al respecto? - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana.
考古学の日本研究者の皆様、ようこそ!今回は、日本と海への汚水問題についてお話しします。
最近、日本が2011年の福島原発事故の処理水を海洋投棄することを国連から許可されたことが世界中のメディアを賑わせている。
タンクは1000基以上、134万トンあり、おそらく容量の98%であろう。また、海水と原発周辺は分析中で、現在はトリチウムの濃度が分析されており、25日の午後に結果が出る予定である。以前は貯水池から水を採取し、安全であるという結果を出していたが、おそらくもっと待つべきだったのだろう。
日本国民が抗議しているのは、これが世界経済に長期的な問題を引き起こすからである。中国が日本産水産物の輸入を全面的に停止したのだから、黙って見過ごすわけがない。 これについてどう思う?
お気に召していただけたなら幸いである。 それではまた、良い一週間を。
Welcome, japonistasarqueologicos to a new installment in which we will talk about the issue of Japan and sewage into the sea, that said, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - It has recently been all over the world's media that Japan has been given the green light by the UN to dump treated water into the Fukushima nuclear power plant from the 2011 accident. - There are more than 1,000 tanks and 1.34 million tons, possibly at 98% of capacity, also the sea water and the surroundings of the nuclear plant are being analysed, currently the concentration of tritium is being analysed, the results will be available on the 25th in the afternoon, previously water samples had been taken from the reservoirs giving as a result that it was safe, but possibly they should have waited longer. - The Japanese people are protesting because this is going to create long-term problems for the world economy. China suspends all imports of Japanese seafood, they are not going to sit back and do nothing. What do you think about this? - I hope you liked it and I'll see you in future posts. Have a good week.
-
 repera23 liked this · 11 months ago
repera23 liked this · 11 months ago -
 corse2b liked this · 11 months ago
corse2b liked this · 11 months ago -
 vivencias-del-alma liked this · 11 months ago
vivencias-del-alma liked this · 11 months ago -
 aloneinthedark-eagle liked this · 11 months ago
aloneinthedark-eagle liked this · 11 months ago -
 u-nobu liked this · 11 months ago
u-nobu liked this · 11 months ago -
 adam-trademark liked this · 11 months ago
adam-trademark liked this · 11 months ago -
 ehlaya liked this · 11 months ago
ehlaya liked this · 11 months ago -
 bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 11 months ago
bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 11 months ago -
 emaadsidiki liked this · 11 months ago
emaadsidiki liked this · 11 months ago -
 noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 11 months ago
noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago
naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago -
 rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago
rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago -
 1-125sec-f8-10feet liked this · 1 year ago
1-125sec-f8-10feet liked this · 1 year ago -
 cchris47 liked this · 1 year ago
cchris47 liked this · 1 year ago -
 shimagoro4056 liked this · 1 year ago
shimagoro4056 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ruinedren52 liked this · 1 year ago
ruinedren52 liked this · 1 year ago -
 radoxon liked this · 1 year ago
radoxon liked this · 1 year ago -
 hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago
hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago -
 sicks93 liked this · 1 year ago
sicks93 liked this · 1 year ago -
 noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago
noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago

238 posts







