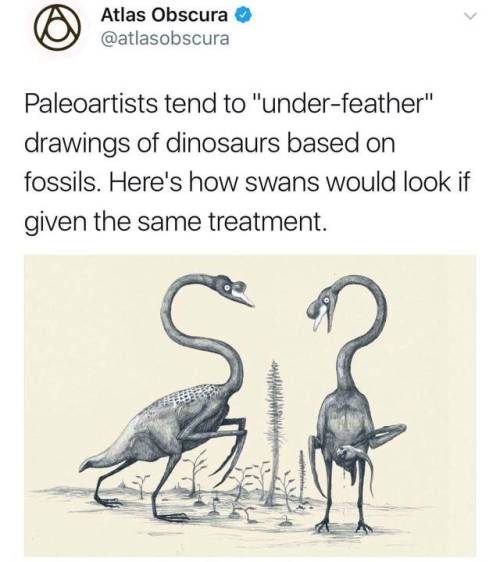
Science-is-magical - Science Is Magic
More Posts from Science-is-magical and Others
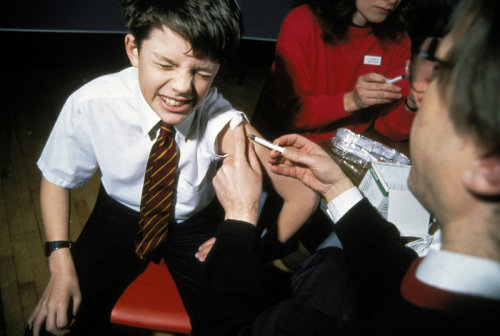
Back in the 1960s, the U.S. started vaccinating kids for measles. As expected, children stopped getting measles.
But something else happened.
Childhood deaths from all infectious diseases plummeted. Even deaths from diseases like pneumonia and diarrhea were cut by half.
“So it’s really been a mystery — why do children stop dying at such high rates from all these different infections following introduction of the measles vaccine,” says Michael Mina, a postdoc in biology at Princeton University and a medical student at Emory University.
Scientists Crack A 50-Year-Old Mystery About The Measles Vaccine Photo credit: Photofusion/UIG via Getty Images

Acting outrageous and making a complete fool of yourself while drunk has been linked to a genetic mutation. It blocks the production of one of the body’s serotonin receptors, which can affect mood swings, impulsive behavior, and decision making. So far, the mutation has only been found in Finnish people, but the discovery is helping researchers understand more about the role serotonin plays in your body. Source Source 2
A reminder that NASA isn’t the only space agency
I have seen many “Space achievements 2015” articles and posts leaving international accomplisments completely out, so here are some of them:
1. A new type of basaltic rock on the moon was found by Chinese robotic lander.
China National Space Administration’s Chang’e-3 landed on the Moon on 14 December 2013, becoming the first spacecraft to soft-land since the Soviet Union‘s Luna 24 in 1976.

2. On February 11, the European Space Agency, ESA, successfully launched on a suborbital trajectory and recovered an experimental wingless glider, IXV.
It became the first true “lifting body” vehicle, which reached a near-orbital speed and then returned back to Earth without any help from wings.

3. On December 9, Japan’s Akatsuki spacecraft succeeded entering orbit of Venus.
Japan Aerospace eXploration Agency’s Akatsuki is the first spacecraft to explore Venus since the ESA’s Venus Express reached the end of its mission in 2014.

4. ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft detected oxygen ‘leaking’ from comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, the first time these molecules have been seen around a comet.
Rosetta spacecraft, the first to drop a lander (named Philae) on a comet, entered orbit around 67P in 2014 and continues to orbit the body. On June 13, European Space Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany, received signals from the Philae lander after months of silence.

5. The Canadian Space Agency has provided NASA with a laser mapping system that will scan an asteroid that could potentially hit the Earth in about 200 years

6. The high-resolution stereo camera on ESA’s Mars Express captured this sweeping view from the planet’s south polar ice cap and across its cratered highlands and beyond.

find Sci-Universe on Tumblr, Instagram & Facebook



Women scientists made up 25% of the Pluto fly-by New Horizon team. Make sure you share this, because erasing women’s achievements in science and history is a tradition. Happens every day.
.
http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/News-Article.php?page=20150712

My tummy is blushing now.
People Were Asked: ‘What’s The Coolest Thing Most People Don’t Know About Their Own Body?’
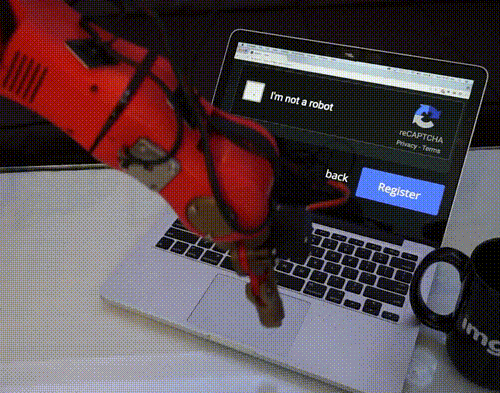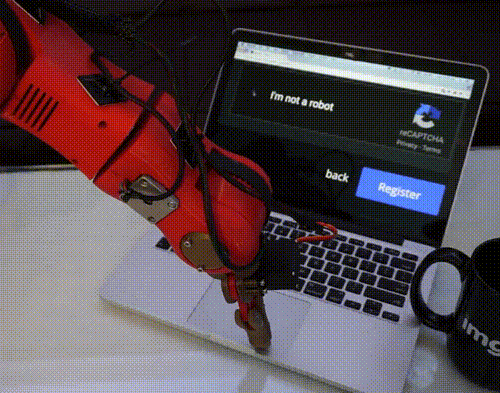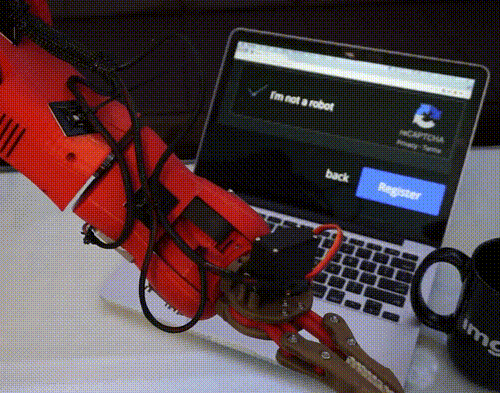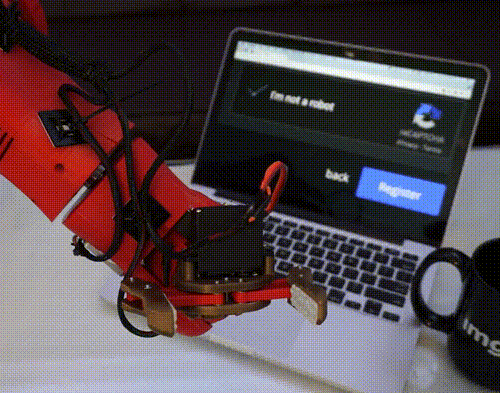
Contamination-seeking drones - IBM Patent 9447448.
Stay back and let the drones do the dirty work. Patent 9447448 makes cognitive drones able to inspect and decontaminate places so humans don’t have to. The drones’ on-board AI system can collect and analyze samples, so it can identify and clean up any bacteria or outbreak. Meanwhile you get to hang back, safely out of harm’s way.
This is just one of the record-breaking 8,000+ patents IBM received this year. Explore the latest IBM patents. →

As Ars has reported previously, scientists have found that triclosan and other antimicrobial soaps have little benefit to consumers and may actually pose risks. These include bolstering antibiotic resistant microbes, giving opportunistic pathogens a leg up, and disrupting microbiomes. In its final ruling, issued Friday, the FDA seemed to agree. “Consumers may think antibacterial washes are more effective at preventing the spread of germs, but we have no scientific evidence that they are any better than plain soap and water,” Janet Woodcock, director of the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), said in a statement. “In fact, some data suggests that antibacterial ingredients may do more harm than good over the long-term.”
[…]
The ruling does not affect alcohol-based hand sanitizers or wipes, which the agency is reviewing separately. It also does not affect antiseptic products used in healthcare settings.
-
 cuttlefishjoe reblogged this · 1 week ago
cuttlefishjoe reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 depraved-kitty reblogged this · 1 week ago
depraved-kitty reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 12catsinadressinggown liked this · 1 week ago
12catsinadressinggown liked this · 1 week ago -
 what-the-fandomm reblogged this · 1 week ago
what-the-fandomm reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 what-the-fandomm liked this · 1 week ago
what-the-fandomm liked this · 1 week ago -
 witch-of-the-waterfall reblogged this · 1 week ago
witch-of-the-waterfall reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 theyhoolikeowls reblogged this · 1 week ago
theyhoolikeowls reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 thesurprisinglyqueertoast reblogged this · 1 week ago
thesurprisinglyqueertoast reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 chaoticpanenergy reblogged this · 1 week ago
chaoticpanenergy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 samiholloway reblogged this · 1 week ago
samiholloway reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 fly-boy reblogged this · 1 week ago
fly-boy reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 no-i-will-not-post liked this · 2 weeks ago
no-i-will-not-post liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 voltronimus-prime liked this · 2 weeks ago
voltronimus-prime liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 rawburrit0 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
rawburrit0 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 trans-ceiver reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
trans-ceiver reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 not-the-conversation-starter reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
not-the-conversation-starter reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 existentially-confused-crow liked this · 2 weeks ago
existentially-confused-crow liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thepppit reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thepppit reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 laqueus reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
laqueus reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 titrationturtle reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
titrationturtle reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 min-is-mini liked this · 2 weeks ago
min-is-mini liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 i-am-mentally-unwell liked this · 2 weeks ago
i-am-mentally-unwell liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 i-am-mentally-unwell reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
i-am-mentally-unwell reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 therefoream liked this · 2 weeks ago
therefoream liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 funkytrashcan reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
funkytrashcan reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 sageisnicethesequel reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
sageisnicethesequel reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 sageisnicethesequel liked this · 2 weeks ago
sageisnicethesequel liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 waiting-for-the-rain-0 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
waiting-for-the-rain-0 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 latias-eevee-hatori reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
latias-eevee-hatori reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 yeahummokay liked this · 2 weeks ago
yeahummokay liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 just-bullshit liked this · 2 weeks ago
just-bullshit liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 fated-normal-767 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
fated-normal-767 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 orisfandomhell reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
orisfandomhell reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 orisfandomhell liked this · 2 weeks ago
orisfandomhell liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 teamfortresstwo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
teamfortresstwo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 that-one-loz-nerd reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
that-one-loz-nerd reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 i-may-be-an-emu liked this · 2 weeks ago
i-may-be-an-emu liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 mulderhiggins reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
mulderhiggins reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 le-random-yeet-up reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
le-random-yeet-up reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 eepy-jazz-musicians liked this · 2 weeks ago
eepy-jazz-musicians liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thegoblinwitch reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
thegoblinwitch reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 anshuist liked this · 2 weeks ago
anshuist liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 leanne132 liked this · 2 weeks ago
leanne132 liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 victoronnie reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
victoronnie reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 solar-megafauna reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
solar-megafauna reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 solar-megafauna liked this · 2 weeks ago
solar-megafauna liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 ryonaprincess1996 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
ryonaprincess1996 reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 mistoquaxo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
mistoquaxo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 undead-sunflower-sys reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
undead-sunflower-sys reblogged this · 2 weeks ago