Astronomers - Blog Posts

Sharp Nebula Shot!
IC 405 & 410 Mosaic - Flame and Tadpole Nebulas


Such a beautiful universe! So much more waiting to be found
Scientists believe they've found evidence of what was once an ocean on Mars. Check out the shoreline on mars!

10 Times More Galaxies!
The universe suddenly looks a lot more crowded…
We already estimated that there were about 100 billion galaxies in the observable universe, but new research shows that this estimate is at least 10 times too low!

First, what is the observable universe? Well, it is the most distant part of the universe we can see from Earth because, in theory, the light from these objects have had time to reach Earth.

In a new study using surveys taken by the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories, astronomers came to the surprising conclusion that there are at least 10 times more galaxies in the observable universe than previously thought. This places the universe’s estimated population at, minimally, 2 trillion galaxies!

The results have clear implications for galaxy formation, and also helps shed light on an ancient astronomical paradox – why is the sky dark at night?
Most of these newly discovered galaxies were relatively small and faint, with masses similar to those of the satellite galaxies surrounding the Milky Way.

Using deep-space images from the Hubble Space Telescope and other observatories, astronomers converted the images into 3-D, in order to make accurate measurements of the number of galaxies at different epochs in the universe’s history.
In addition, they used new mathematical models, which allowed them to infer the existence of galaxies that the current generation of telescopes cannot observe. This led to the surprising conclusion that in order for the numbers of galaxies we now see and their masses to add up, there must be a further 90% of galaxies in the observable universe that are too faint and too far away to be seen with present-day telescopes.

The myriad small faint galaxies from the early universe merged over time into the larger galaxies we can now observe.
That means that over 90% of the galaxies in the universe have yet to be studied! In the near future, the James Webb Space Telescope will be able to study these ultra-faint galaxies and give us more information about their existence.

So back to the question…Why is the sky dark at night if the universe contains an infinity of stars? Researchers came to the conclusion that indeed there actually is such an abundance of galaxies that, in principle, every patch in the sky contains part of a galaxy.
However, starlight from the galaxies is invisible to the human eye and most modern telescopes due to other known factors that reduce visible and ultraviolet light in the universe. Those factors are the reddening of light due to the expansion of space, the universe’s dynamic nature, and the absorption of light by intergalactic dust and gas. All combined, this keeps the night sky dark to our vision.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
At Least 94 More Exoplanets were just recently discovered by Astronomers and Astrophysicists using NASA's Kepler Space_Telescope.
Scientists discover almost 100 new exoplanets
“We started out analyzing 275 candidates of which 149 were validated as real exoplanets. In turn 95 of these planets have proved to be new discoveries,” said American PhD student Andrew Mayo at the National Space Institute (DTU Space) at the Technical University of Denmark.

“This research has been underway since the first K2 data release in 2014.”
Mayo is the main author of the work being presented in the Astronomical Journal.
The research has been conducted partly as a senior project during his undergraduate studies at Harvard College. It has also involved a team of international colleagues from institutions such as NASA, Caltech, UC Berkeley, the University of Copenhagen, and the University of Tokyo.
Keep reading





Feeling stressed? Imagine being squeezed into a point smaller than an atom! 😱 That's what happens at the heart of a black hole. Swipe ➡️ through this post to learn how these cosmic wonders are formed! 🌌✨

Vera Rubin (b. 1928)
When Vera Cooper Rubin told her high school physics teacher that she’d been accepted to Vassar, he said, “That’s great. As long as you stay away from science, it should be okay.”
Rubin graduated Phi Beta Kappa in 1948, the only astronomy major in her class at Vassar, and went on to receive her master’s from Cornell in 1950 (after being turned away by Princeton because they did not allow women in their astronomy program) and her Ph.D. from Georgetown in 1954. Now a senior researcher at the Carnegie Institute’s Department of Terrestrial Magnetism, Rubin is credited with proving the existence of “dark matter,” or nonluminous mass, and forever altering our notions of the universe. She did so by gathering irrefutable evidence to persuade the astronomical community that galaxies spin at a faster speed than Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation allows. As a result of this finding, astronomers conceded that the universe must be filled with more material than they can see.
Rubin made a name for herself not only as an astronomer but also as a woman pioneer; she fought through severe criticisms of her work to eventually be elected to the National Academy of Sciences (at the time, only three women astronomers were members) and to win the highest American award in science, the National Medal of Science. Her master’s thesis, presented to a 1950 meeting of the American Astronomical Society, met with severe criticism, and her doctoral thesis was essentially ignored, though her conclusions were later validated. “Fame is fleeting,” Rubin said when she was elected to the National Academy of Sciences. “My numbers mean more to me than my name. If astronomers are still using my data years from now, that’s my greatest compliment.”
Sources:
1. http://innovators.vassar.edu/innovator.html?id=68; http://science.vassar.edu/women/
2. http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/45424



The Boogeyman Nebula and Tarantula Nebula
since I haven't reblogged much space lately
Here ya go <3


Alright ladies and gents! NEW MARS IMAGES
Check out brand new photos of the small moon Phobos! Mars Express Captures Stunning Image of Phobos, Olympus Mons, and Mars’ Atmosphere
⚠️remember to click on photos to view full 4k quality.












1200 Megapixel
⚠️Remember to click on photo to view in full hd quality
Jupiters moons rotating! Look at those spinning clouds! Thanks to Cassini
I can't tell if these are all real but they are all so gorgeous!!
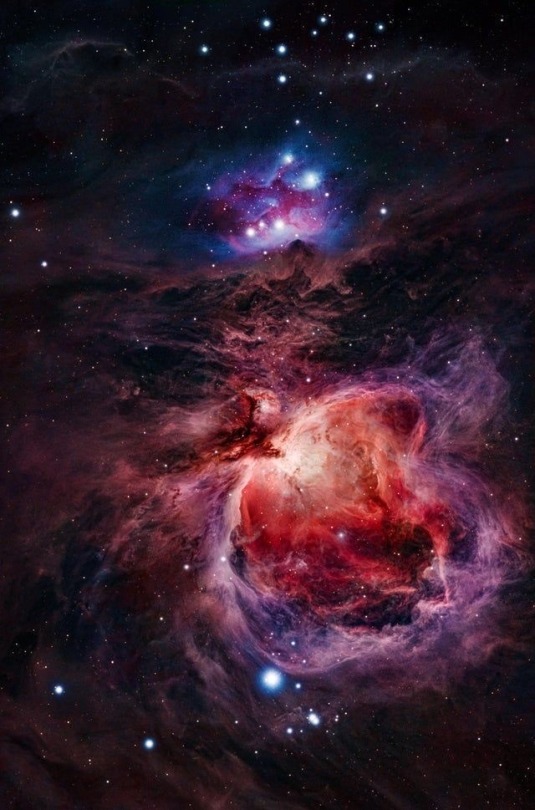
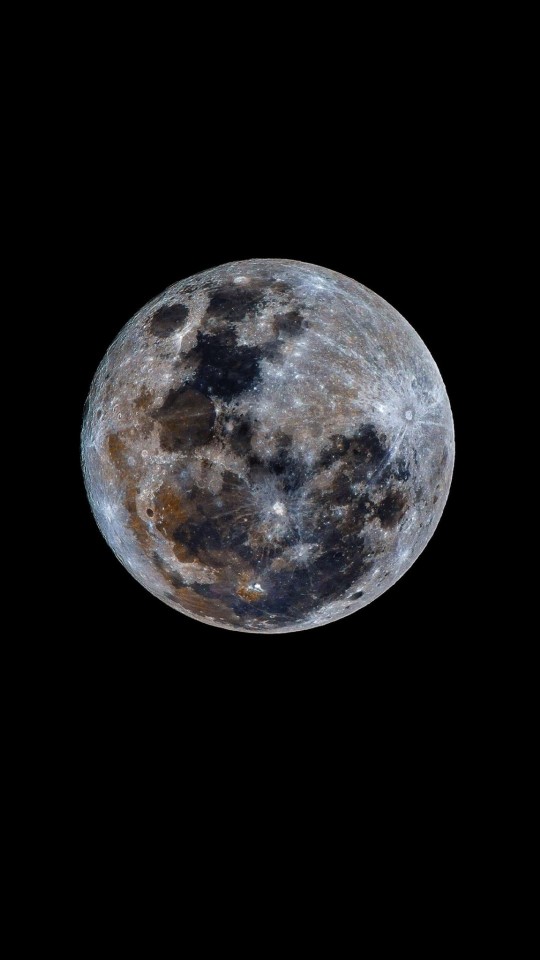









Our Moon in stunning 8K

NGC 6914 - 14.5 hrs SHO w/rgb stars
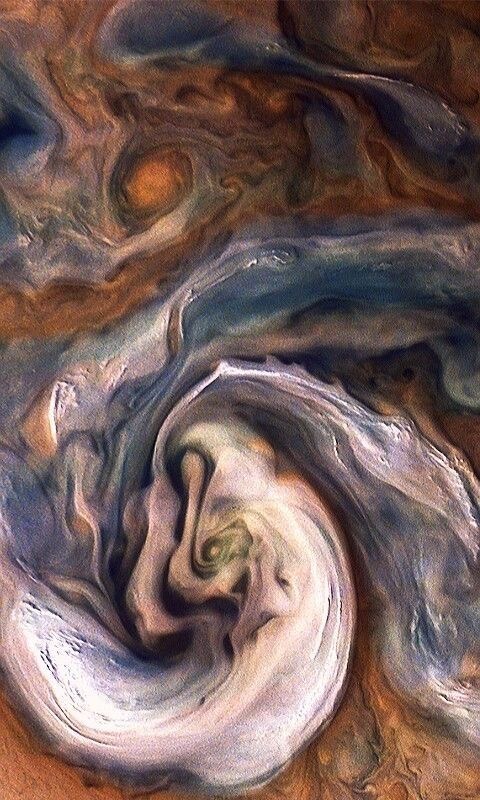
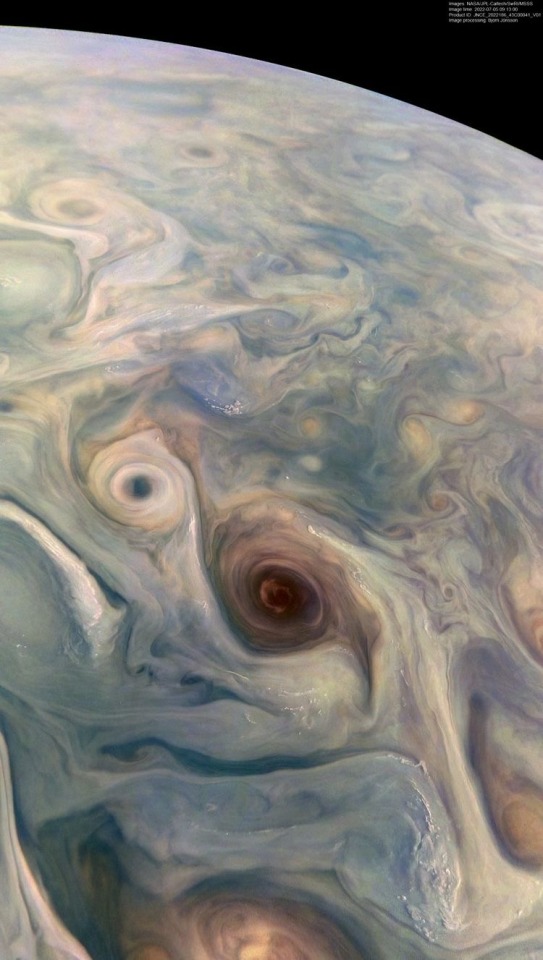
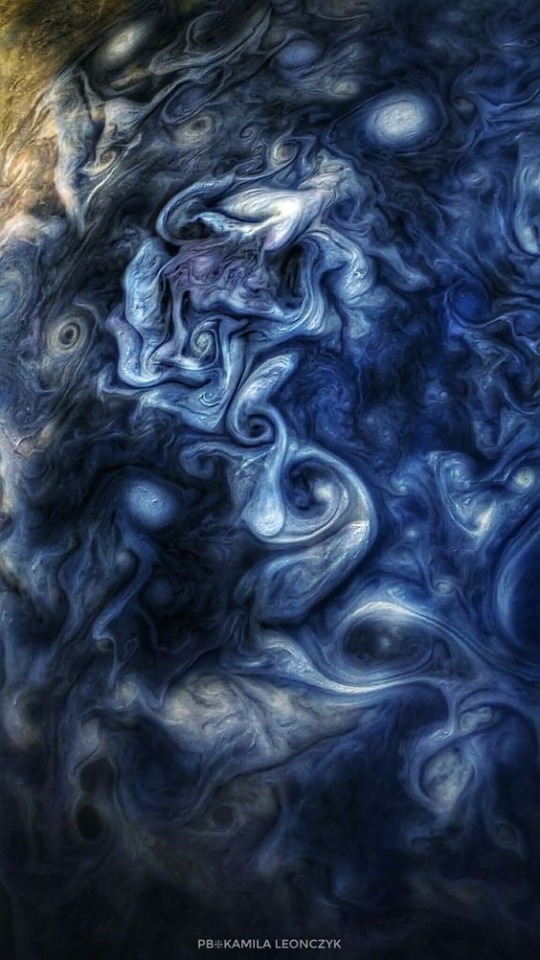
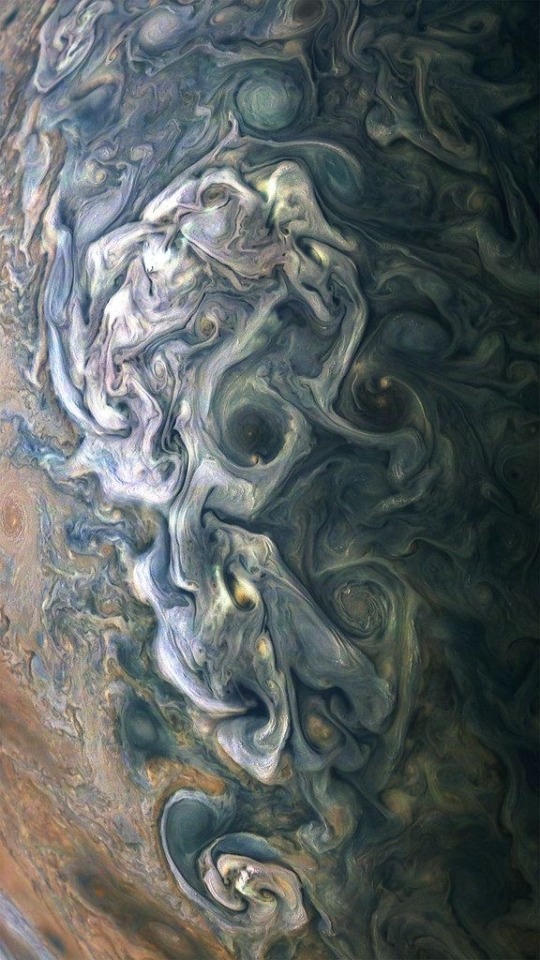









My favorite most beautiful planet in the solar system! Jupiter!
